Page 89 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 89
THERMOPLASTICS
THERMOPLASTICS 2.29
LDPE. Table 2.5 compares mechanical properties of LLDPE to LDPE. As is the case with
LDPE, film accounts for approximately three-quarters of the consumption of LLDPE. As
the name implies, it is a long linear chain without long side chains or branches. The short
chains, which are present, disrupt the polymer chain uniformity enough to prevent crystal-
line formation and hence prevent the polymer from achieving high densities. Develop-
ments of the past decade have enabled production economies compared to LDPE due to
lower polymerization pressures and temperatures. A typical LDPE process requires
35,000 psi, which is reduced to 300 psi in the case of LLDPE, and reaction temperatures
as low as 100°C rather than 200 or 300°C are used. LLDPE is actually a copolymer con-
taining side branches of 1-butene most commonly, with 1-hexene or 1-octene also present.
3
Density ranges of 0.915 to 0.940 g/cm are polymerized with Ziegler catalysts, which ori-
ent the polymer chain and govern the tacticity of the pendant side groups. 222
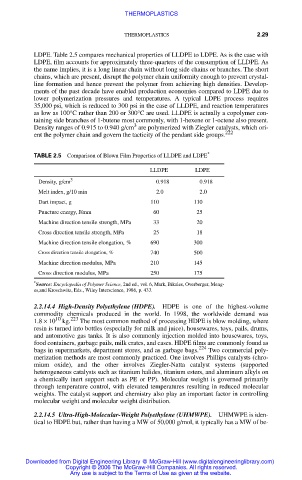
TABLE 2.5 Comparison of Blown Film Properties of LLDPE and LDPE *
LLDPE LDPE
Density, g/cm 3 0.918 0.918
Melt index, g/10 min 2.0 2.0
Dart impact, g 110 110
Puncture energy, J/mm 60 25
Machine direction tensile strength, MPa 33 20
Cross direction tensile strength, MPa 25 18
Machine direction tensile elongation, % 690 300
Cross direction tensile elongation, % 740 500
Machine direction modulus, MPa 210 145
Cross direction modulus, MPa 250 175
*
Source: Encyclopedia of Polymer Science, 2nd ed., vol. 6, Mark, Bikales, Overberger, Meng-
es,and Kroschwitz, Eds., Wiley Interscience, 1986, p. 433.
2.2.14.4 High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE). HDPE is one of the highest-volume
commodity chemicals produced in the world. In 1998, the worldwide demand was
10
1.8 × 10 kg. 223 The most common method of processing HDPE is blow molding, where
resin is turned into bottles (especially for milk and juice), housewares, toys, pails, drums,
and automotive gas tanks. It is also commonly injection molded into housewares, toys,
food containers, garbage pails, milk crates, and cases. HDPE films are commonly found as
bags in supermarkets, department stores, and as garbage bags. 224 Two commercial poly-
merization methods are most commonly practiced. One involves Phillips catalysts (chro-
mium oxide), and the other involves Ziegler-Natta catalyst systems (supported
heterogeneous catalysts such as titanium halides, titanium esters, and aluminum alkyls on
a chemically inert support such as PE or PP). Molecular weight is governed primarily
through temperature control, with elevated temperatures resulting in reduced molecular
weights. The catalyst support and chemistry also play an important factor in controlling
molecular weight and molecular weight distribution.
2.2.14.5 Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE). UHMWPE is iden-
tical to HDPE but, rather than having a MW of 50,000 g/mol, it typically has a MW of be-
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.