Page 169 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 169
146 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
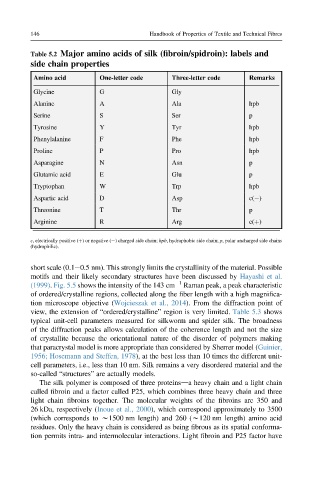
Table 5.2 Major amino acids of silk (fibroin/spidroin): labels and
side chain properties
Amino acid One-letter code Three-letter code Remarks
Glycine G Gly
Alanine A Ala hpb
Serine S Ser p
Tyrosine Y Tyr hpb
Phenylalanine F Phe hpb
Proline P Pro hpb
Asparagine N Asn p
Glutamic acid E Glu p
Tryptophan W Trp hpb
Aspartic acid D Asp c( )
Threonine T Thr p
Arginine R Arg c(þ)
c, electrically positive (þ) or negative ( ) charged side chain; hpb, hydrophobic side chain; p, polar uncharged side chains
(hydrophilic).
short scale (0.1e0.5 nm). This strongly limits the crystallinity of the material. Possible
motifs and their likely secondary structures have been discussed by Hayashi et al.
(1999). Fig. 5.5 shows the intensity of the 143 cm 1 Raman peak, a peak characteristic
of ordered/crystalline regions, collected along the fiber length with a high magnifica-
tion microscope objective (Wojcieszak et al., 2014). From the diffraction point of
view, the extension of “ordered/crystalline” region is very limited. Table 5.3 shows
typical unit-cell parameters measured for silkworm and spider silk. The broadness
of the diffraction peaks allows calculation of the coherence length and not the size
of crystallite because the orientational nature of the disorder of polymers making
that paracrystal model is more appropriate than considered by Sherrer model (Guinier,
1956; Hosemann and Steffen, 1978), at the best less than 10 times the different unit-
cell parameters, i.e., less than 10 nm. Silk remains a very disordered material and the
so-called “structures” are actually models.
The silk polymer is composed of three proteinsda heavy chain and a light chain
called fibroin and a factor called P25, which combines three heavy chain and three
light chain fibroins together. The molecular weights of the fibroins are 350 and
26 kDa, respectively (Inoue et al., 2000), which correspond approximately to 3500
(which corresponds to w1500 nm length) and 260 (w120 nm length) amino acid
residues. Only the heavy chain is considered as being fibrous as its spatial conforma-
tion permits intra- and intermolecular interactions. Light fibroin and P25 factor have