Page 172 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 172
Silk: fibers, films, and compositesdtypes, processing, structure, and mechanics 149
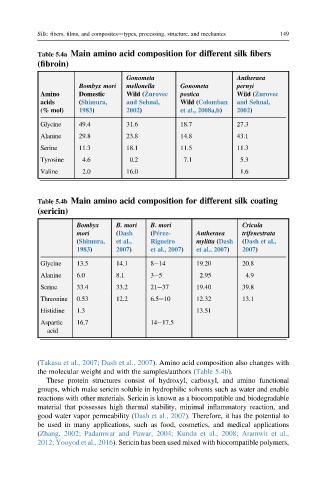
Table 5.4a Main amino acid composition for different silk fibers
(fibroin)
Gonometa Antheraea
Bombyx mori mellonella Gonometa pernyi
Amino Domestic Wild (Zurovec postica Wild (Zurovec
acids (Shimura, and Sehnal, Wild (Colomban and Sehnal,
(% mol) 1983) 2002) et al., 2008a,b) 2002)
Glycine 49.4 31.6 18.7 27.3
Alanine 29.8 23.8 14.8 43.1
Serine 11.3 18.1 11.5 11.3
Tyrosine 4.6 0.2 7.1 5.3
Valine 2.0 16.0 1.6
Table 5.4b Main amino acid composition for different silk coating
(sericin)
Bombyx B. mori B. mori Cricula
mori (Dash (Pérez- Antheraea trifenestrata
(Shimura, et al., Rigueiro mylitta (Dash (Dash et al.,
1983) 2007) et al., 2007) et al., 2007) 2007)
Glycine 13.5 14.1 8e14 19.20 20.8
Alanine 6.0 8.1 3e5 2.95 4.9
Serine 33.4 33.2 21e37 19.40 39.8
Threonine 0.53 12.2 6.5e10 12.32 13.1
Histidine 1.3 13.51
Aspartic 16.7 14e17.5
acid
(Takasu et al., 2007; Dash et al., 2007). Aminoacidcompositionalsochanges with
the molecular weight and with the samples/authors (Table 5.4b).
These protein structures consist of hydroxyl, carboxyl, and amino functional
groups, which make sericin soluble in hydrophilic solvents such as water and enable
reactions with other materials. Sericin is known as a biocompatible and biodegradable
material that possesses high thermal stability, minimal inflammatory reaction, and
good water vapor permeability (Dash et al., 2007). Therefore, it has the potential to
be used in many applications, such as food, cosmetics, and medical applications
(Zhang, 2002; Padamwar and Pawar, 2004; Kundu et al., 2008; Aramwit et al.,
2012; Yooyod et al., 2016). Sericin has been used mixed with biocompatible polymers,