Page 170 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 170
Silk: fibers, films, and compositesdtypes, processing, structure, and mechanics 147
(a) (a') (b)
0.4 nm
3.8 nm
0.4 nm
7.3 nm
Turn
Extended
chain
0.40 nm
α helix =>
Regular
helix ‘β’ extended chain
0
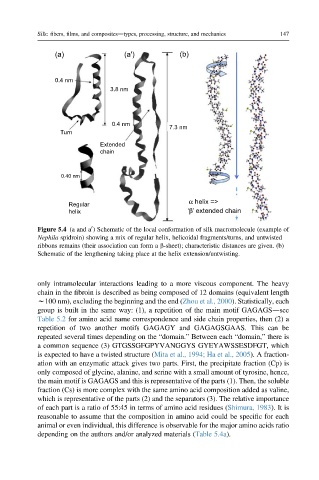
Figure 5.4 (a and a ) Schematic of the local conformation of silk macromolecule (example of
Nephila spidroin) showing a mix of regular helix, helicoidal fragments/turns, and untwisted
ribbons remains (their association can form a b-sheet); characteristic distances are given. (b)
Schematic of the lengthening taking place at the helix extension/untwisting.
only intramolecular interactions leading to a more viscous component. The heavy
chain in the fibroin is described as being composed of 12 domains (equivalent length
w100 nm), excluding the beginning and the end (Zhou et al., 2000). Statistically, each
group is built in the same way: (1), a repetition of the main motif GAGAGSdsee
Table 5.2 for amino acid name correspondence and side chain properties, then (2) a
repetition of two another motifs GAGAGY and GAGAGSGAAS. This can be
repeated several times depending on the “domain.” Between each “domain,” there is
a common sequence (3) GTGSSGFGPYVANGGYS GYEYAWSSESDFGT, which
is expected to have a twisted structure (Mita et al., 1994; Ha et al., 2005). A fraction-
ation with an enzymatic attack gives two parts. First, the precipitate fraction (Cp) is
only composed of glycine, alanine, and serine with a small amount of tyrosine, hence,
the main motif is GAGAGS and this is representative of the parts (1). Then, the soluble
fraction (Cs) is more complex with the same amino acid composition added as valine,
which is representative of the parts (2) and the separators (3). The relative importance
of each part is a ratio of 55:45 in terms of amino acid residues (Shimura, 1983). It is
reasonable to assume that the composition in amino acid could be specific for each
animal or even individual, this difference is observable for the major amino acids ratio
depending on the authors and/or analyzed materials (Table 5.4a).