Page 210 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 210
Engineering properties of spider silk 187
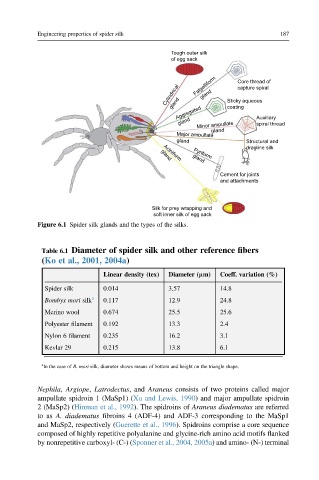
Tough outer silk
of egg sack
Core thread of
Cylindrical Falgelliform Sticky aqueous
capture spiral
gland
gland
Aggregated coating Auxiliary
gland Minor ampullate spiral thread
gland
Major ampullate
gland Structural and
dragline silk
Pyriform
gland
Aciniform
gland
Cement for joints
and attachments
Silk for prey wrapping and
soft inner silk of egg sack
Figure 6.1 Spider silk glands and the types of the silks.
Table 6.1 Diameter of spider silk and other reference fibers
(Ko et al., 2001, 2004a)
Linear density (tex) Diameter (mm) Coeff. variation (%)
Spider silk 0.014 3.57 14.8
Bombyx mori silk a 0.117 12.9 24.8
Merino wool 0.674 25.5 25.6
Polyester filament 0.192 13.3 2.4
Nylon 6 filament 0.235 16.2 3.1
Kevlar 29 0.215 13.8 6.1
a
In the case of B. mori silk, diameter shows means of bottom and height on the triangle shape.
Nephila, Argiope, Latrodectus, and Araneus consists of two proteins called major
ampullate spidroin 1 (MaSp1) (Xu and Lewis, 1990) and major ampullate spidroin
2 (MaSp2) (Hinman et al., 1992). The spidroins of Araneus diadematus are referred
to as A. diadematus fibroins 4 (ADF-4) and ADF-3 corresponding to the MaSp1
and MaSp2, respectively (Guerette et al., 1996). Spidroins comprise a core sequence
composed of highly repetitive polyalanine and glycine-rich amino acid motifs flanked
by nonrepetitive carboxyl- (C-) (Sponner et al., 2004, 2005a) and amino- (N-) terminal