Page 232 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 232
Engineering properties of spider silk 207
6.4 Other engineering properties
An examination of the literature shows that the majority of mechanical studies are
focused on the tensile properties of spider silk fibers with the exception of Zemlin’s
torsional measurement (Zemlin, 1968). Characterization of other engineering prop-
erties of spider silk such as compression and torsion properties was made possible
by using an ultrasensitive micromeasurement fiber testing system developed by
Kawabata (1996).
6.4.1 Transverse compression properties
The compression tests in the transverse fiber diameter direction were carried out by
placing a single fiber between a flat and mirror-finished steel plate and a mirror-
finished 0.2 mm square compression plane. Because of the fineness of the spider fiber,
a combination of sensitive instrumentation and mechanistic analysis are required in
order to assure accurate measurement of the compressive stress-stain properties. A
description of the compression tester has been detailed by Kawabata (1996).
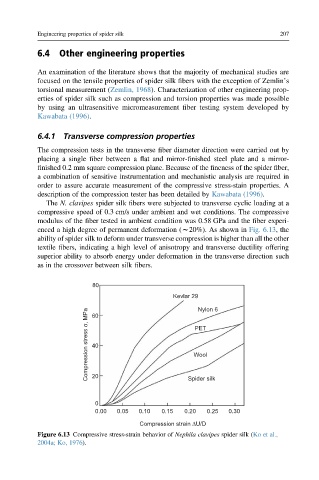
The N. clavipes spider silk fibers were subjected to transverse cyclic loading at a
compressive speed of 0.3 cm/s under ambient and wet conditions. The compressive
modulus of the fiber tested in ambient condition was 0.58 GPa and the fiber experi-
enced a high degree of permanent deformation (w20%). As shown in Fig. 6.13, the
ability of spider silk to deform under transverse compression is higher than all the other
textile fibers, indicating a high level of anisotropy and transverse ductility offering
superior ability to absorb energy under deformation in the transverse direction such
as in the crossover between silk fibers.
80
Kevlar 29 Nylon 6
Compression stress σ, MPa 40 Wool
60
PET
20
0 Spider silk
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30
Compression strain ΔU/D
Figure 6.13 Compressive stress-strain behavior of Nephila clavipes spider silk (Ko et al.,
2004a; Ko, 1976).