Page 388 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 388
Structure and behavior of collagen fibers 361
30
Weighted displacement (µm) 20
25
15
10
0 5
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 11.8 Vibrational analysis of decellularized dermis. A plot of weighted displacement
versus vibration frequency is used to determine the resonant frequency. The resonant
frequency is determined from measurement of the maximum displacement of a sample vibrated
between 0 and 700 HZ. Note the maximum displacement is measured and converted into a
vibrational modulus using the calibration curve shown in Fig. 11.9. The modulus measured at
the resonant frequency is very close to the elastic modulus.
Reprinted from Shah R, Pierce MC, Silver FH: A method for non-destructive mechanical testing
of tissues and implants, J Biomed Mat Res Part A, 2016.
16,000,000
14,000,000
Vibrational modulus (Pa) 10,000,000 y = 1.1968x – 125344
12,000,000
2
R = 0.9073
8,000,000
6,000,000
4,000,000
2,000,000
0
0 2,000,000 4,000,000 6,000,000 8,000,000 10,000,000
Tensile modulus (Pa)
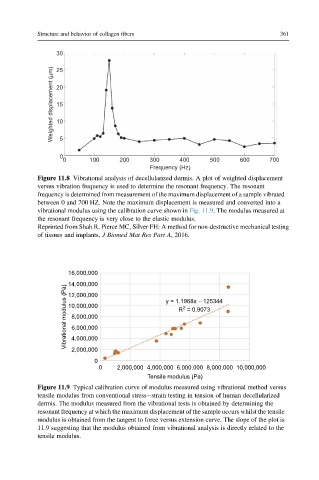
Figure 11.9 Typical calibration curve of modulus measured using vibrational method versus
tensile modulus from conventional stressestrain testing in tension of human decellularized
dermis. The modulus measured from the vibrational tests is obtained by determining the
resonant frequency at which the maximum displacement of the sample occurs whilst the tensile
modulus is obtained from the tangent to force versus extension curve. The slope of the plot is
11.9 suggesting that the modulus obtained from vibrational analysis is directly related to the
tensile modulus.