Page 406 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 406
The chemistry, manufacture, and tensile behavior of polyamide fibers 379
of the high melting temperature phase increases with PA 6 concentration in the spin-
ning solution. The morphological crystalline unit is lamellae (see Fig. 12.9). The
thickness of the lamellae depends on the crystallization temperature and it is usually
around 6e10 nm. The macromolecules are normal to the lamellae and are folded
back and forth on themselves. A single-polymer molecule may belong to more than
one lamella, especially in polymers crystallized from the melt (Yang, 2006).
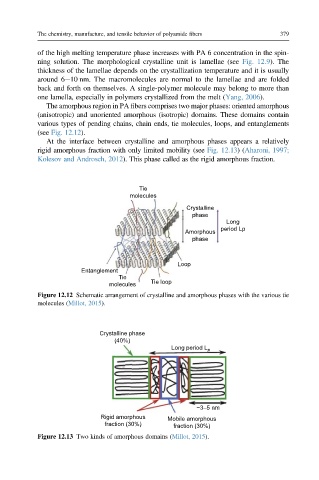
The amorphous region in PA fibers comprises two major phases: oriented amorphous
(anisotropic) and unoriented amorphous (isotropic) domains. These domains contain
various types of pending chains, chain ends, tie molecules, loops, and entanglements
(see Fig. 12.12).
At the interface between crystalline and amorphous phases appears a relatively
rigid amorphous fraction with only limited mobility (see Fig. 12.13)(Aharoni, 1997;
Kolesov and Androsch, 2012). This phase called as the rigid amorphous fraction.
Tie
molecules
Crystalline
phase
Long
period Lp
Amorphous
phase
Loop
Entanglement
Tie
molecules Tie loop
Figure 12.12 Schematic arrangement of crystalline and amorphous phases with the various tie
molecules (Millot, 2015).
Crystalline phase
(40%) Long period L p
~3–5 nm
Rigid amorphous Mobile amorphous
fraction (30%) fraction (30%)
Figure 12.13 Two kinds of amorphous domains (Millot, 2015).