Page 403 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 403
376 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
Antiparallel chains
Crystallographic unit
Chemical
unit
N–C
α form
C–N
PA 6
N–C O
γ form C
H
N–C
N
Parallel chains
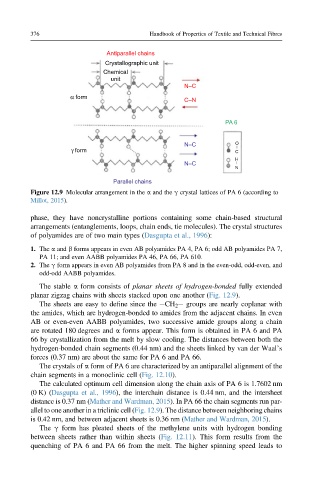
Figure 12.9 Molecular arrangement in the a and the g crystal lattices of PA 6 (according to
Millot, 2015).
phase, they have noncrystalline portions containing some chain-based structural
arrangements (entanglements, loops, chain ends, tie molecules). The crystal structures
of polyamides are of two main types (Dasgupta et al., 1996):
1. The a and b forms appears in even AB polyamides PA 4, PA 6; odd AB polyamides PA 7,
PA 11; and even AABB polyamides PA 46, PA 66, PA 610.
2. The g form appears in even AB polyamides from PA 8 and in the even-odd, odd-even, and
odd-odd AABB polyamides.
The stable a form consists of planar sheets of hydrogen-bonded fully extended
planar zigzag chains with sheets stacked upon one another (Fig. 12.9).
The sheets are easy to define since the eCH 2 e groups are nearly coplanar with
the amides, which are hydrogen-bonded to amides from the adjacent chains. In even
AB or even-even AABB polyamides, two successive amide groups along a chain
are rotated 180 degrees and a forms appear. This form is obtained in PA 6 and PA
66 by crystallization from the melt by slow cooling. The distances between both the
hydrogen-bonded chain segments (0.44 nm) and the sheets linked by van der Waal’s
forces (0.37 nm) are about the same for PA 6 and PA 66.
The crystals of a form of PA 6 are characterized by an antiparallel alignment of the
chain segments in a monoclinic cell (Fig. 12.10).
The calculated optimum cell dimension along the chain axis of PA 6 is 1.7602 nm
(0 K) (Dasgupta et al., 1996), the interchain distance is 0.44 nm, and the intersheet
distance is 0.37 nm (Mather and Wardman, 2015). In PA 66 the chain segments run par-
allel to one another in a triclinic cell (Fig. 12.9). The distance between neighboring chains
is 0.42 nm, and between adjacent sheets is 0.36 nm (Mather and Wardman, 2015).
The g form has pleated sheets of the methylene units with hydrogen bonding
between sheets rather than within sheets (Fig. 12.11). This form results from the
quenching of PA 6 and PA 66 from the melt. The higher spinning speed leads to