Page 402 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 402
The chemistry, manufacture, and tensile behavior of polyamide fibers 375
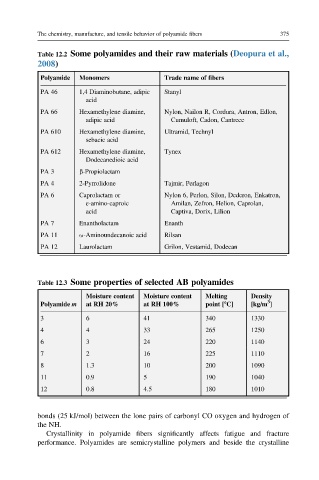
Table 12.2 Some polyamides and their raw materials (Deopura et al.,
2008)
Polyamide Monomers Trade name of fibers
PA 46 1,4 Diaminobutane, adipic Stanyl
acid
PA 66 Hexamethylene diamine, Nylon, Nailon R, Cordura, Antron, Edlon,
adipic acid Cumuloft, Cadon, Cantrece
PA 610 Hexamethylene diamine, Ultramid, Technyl
sebacic acid
PA 612 Hexamethylene diamine, Tynex
Dodecanedioic acid
PA 3 b-Propiolactam
PA 4 2-Pyrrolidone Tajmir, Perlagon
PA 6 Caprolactam or Nylon 6, Perlon, Silon, Dederon, Enkatron,
ε-amino-caproic Amilan, Zefron, Helion, Caprolan,
acid Captiva, Dorix, Lilion
PA 7 Enantholactam Enanth
PA 11 u-Aminoundecanoic acid Rilsan
PA 12 Laurolactam Grilon, Vestamid, Dodecan
Table 12.3 Some properties of selected AB polyamides
Moisture content Moisture content Melting Density
Polyamide m at RH 20% at RH 100% point [8C] [kg/m ]
3
3 6 41 340 1330
4 4 33 265 1250
6 3 24 220 1140
7 2 16 225 1110
8 1.3 10 200 1090
11 0.9 5 190 1040
12 0.8 4.5 180 1010
bonds (25 kJ/mol) between the lone pairs of carbonyl CO oxygen and hydrogen of
the NH.
Crystallinity in polyamide fibers significantly affects fatigue and fracture
performance. Polyamides are semicrystalline polymers and beside the crystalline