Page 397 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 397
370 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
p H N–(CH ) –NH + p COOH–(CH ) – COOH
2
2 n–2
2
2 m
Diamine (m carbon atom) dicarboxylic acid (n carbon atom)
→ [–NH– (CH ) –NH–CO–(CH ) –CO– ] + 2p H O
2 m 2 n–2 p 2
AABB polyamides PA mn
p = no. of molecules and ultimately it is the degree of polymerization
p H N–(CH ) –COOH → [ –H N–(CH ) –CO–] + p H O
2
2
2 m–1
p
2
2 m–1
Amino acid (m carbon atom)
AB polyamides PA m
CO
2
p (CH ) n–1
[ NH – (CH ) – CO – ]
2 n–1
NH
Figure 12.4 Chemical compositions of polyamides.
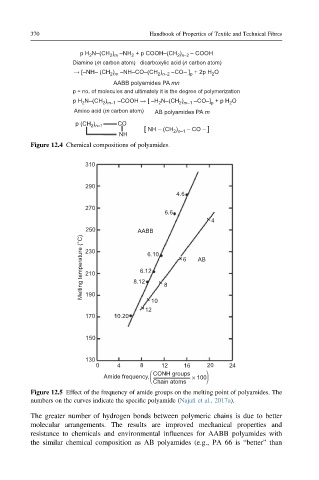
310
290
4.6
270
6.6
4
250 AABB
Melting temperature (°C) 230 8.12 6.10 6 AB
6.12
210
190
10 8
12
170 10.20
150
130
0 4 8 12 16 20 24
CONH groups
Amide frequency, × 100
Chain atoms
Figure 12.5 Effect of the frequency of amide groups on the melting point of polyamides. The
numbers on the curves indicate the specific polyamide (Najafi et al., 2017a).
The greater number of hydrogen bonds between polymeric chains is due to better
molecular arrangements. The results are improved mechanical properties and
resistance to chemicals and environmental influences for AABB polyamides with
the similar chemical composition as AB polyamides (e.g., PA 66 is “better” than