Page 128 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 128
8.1 Methods and mechanisms of surface cleaning 123
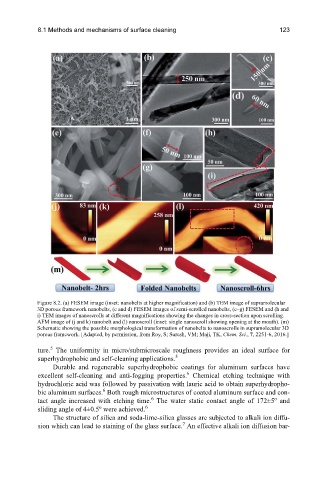
Figure 8.2. (a) FESEM image (inset: nanobelts at higher magnification) and (b) TEM image of supramolecular
3D porous framework nanobelts, (c and d) FESEM images of semi-scrolled nanobelts, (e–g) FESEM and (h and
i) TEM images of nanoscrolls at different magnifications showing the changes in cross-section upon scrolling.
AFM image of (j and k) nanobelt and (l) nanoscroll (inset: single nanoscroll showing opening at the mouth). (m)
Schematic showing the possible morphological transformation of nanobelts to nanoscrolls in supramolecular 3D
porous framework. [Adapted, by permission, from Roy, S; Suresh, VM; Maji, TK, Chem. Sci., 7, 2251-6, 2016.]
5
ture. The uniformity in micro/submicroscale roughness provides an ideal surface for
5
superhydrophobic and self-cleaning applications.
Durable and regenerable superhydrophobic coatings for aluminum surfaces have
6
excellent self-cleaning and anti-fogging properties. Chemical etching technique with
hydrochloric acid was followed by passivation with lauric acid to obtain superhydropho-
6
bic aluminum surfaces. Both rough microstructures of coated aluminum surface and con-
6
o
tact angle increased with etching time. The water static contact angle of 172±5 and
6
o
sliding angle of 4±0.5 were achieved.
The structure of silica and soda-lime-silica glasses are subjected to alkali ion diffu-
7
sion which can lead to staining of the glass surface. An effective alkali ion diffusion bar-