Page 96 - Hardware Implementation of Finite-Field Arithmetic
P. 96
mod m Operations 79
First represent 202 in binary: x = 11001010. Then compute
p = 0
a = 0 + 0 · 236 = 0, p = a/2 = 0
a = 0 + 1 · 236 = 236, p = a/2 = 118
a = 118 + 0 · 236 = 118, p = a/2 = 59
a = 59 + 1 · 236 = 295, p = (a + m)/2 = 534/2 = 267
a = 267 + 0 · 236 = 267, p = (a + m)/2 = 506/2 = 253
a = 253 + 0 · 236 = 253, p = (a + m)/2 = 492/2 = 246
a = 246 + 1 · 236 = 482, p = a/2 = 241
a = 241 + 1 · 236 = 477, p = (a + m)/2 = 716/2 = 358
As 358 ≥ m, the final result is 358 − 239 = 119.
An executable Ada file binary_Montgomery_product.adb, includ-
ing Algorithm 3.12, is available at www.arithmetic-circuits.org.
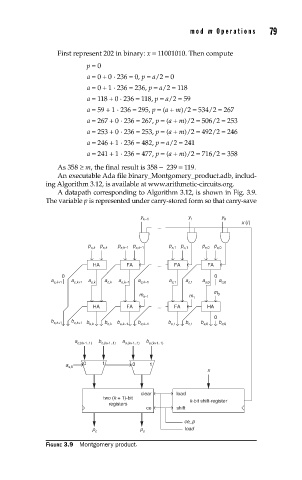
A datapath corresponding to Algorithm 3.12, is shown in Fig. 3.9.
The variable p is represented under carry-stored form so that carry-save
y k–1 y 1 y 0
x (i )
...
p c,k p s,k p s,k–1 p c,k–1 p s,1 p c,1 p s,0 p c,0
HA FA ... FA FA
0 0
a s,k+1 a c,k+1 a s,k a c,k a s,k–1 a c,k–1 a s,1 a c,1 a s,0 a c,0
m 0
m k–1
m 1
HA FA ... FA HA
0
b s,k+1 b c,k+1
b s,k b c,k b s,k–1 b c,k–1 b s,1 b c,1 b s,0 b c,0
a c,(k+1..1) b c,(k+1..1) a s,(k+1..1) b s,(k+1..1)
0 1 0 1
a s,0
x
clear load
two (k + 1)-bit k-bit shift-register
registers
ce shift
ce_p
load
p c p s
FIGURE 3.9 Montgomery product .