Page 31 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 31
4 G a s , C h e m i c a l , a n d F r e e - E l e c t r o n L a s e r s Carbon Dioxide Lasers 5
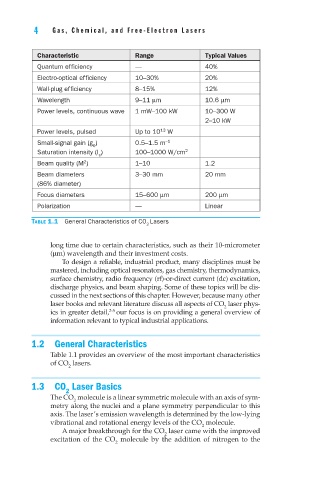
Characteristic Range Typical Values
Quantum efficiency — 40%
Electro-optical efficiency 10–30% 20%
Wall-plug efficiency 8–15% 12%
Wavelength 9–11 µm 10.6 µm
Power levels, continuous wave 1 mW–100 kW 10–300 W
2–10 kW
Power levels, pulsed Up to 10 W
13
Small-signal gain (g ) 0.5–1.5 m –1
0
Saturation intensity (I ) 100–1000 W/cm 2
s
2
Beam quality (M ) 1–10 1.2
Beam diameters 3–30 mm 20 mm
(86% diameter)
Focus diameters 15–600 µm 200 µm
Polarization — Linear
Table 1.1 General Characteristics of CO Lasers
2
long time due to certain characteristics, such as their 10-micrometer
(µm) wavelength and their investment costs.
To design a reliable, industrial product, many disciplines must be
mastered, including optical resonators, gas chemistry, thermodynamics,
surface chemistry, radio frequency (rf)-or-direct current (dc) excitation,
discharge physics, and beam shaping. Some of these topics will be dis-
cussed in the next sections of this chapter. However, because many other
laser books and relevant literature discuss all aspects of CO laser phys-
2
ics in greater detail, 2-5 our focus is on providing a general overview of
information relevant to typical industrial applications.
1.2 General Characteristics
Table 1.1 provides an overview of the most important characteristics
of CO lasers.
2
1.3 CO Laser Basics
2
The CO molecule is a linear symmetric molecule with an axis of sym-
2
metry along the nuclei and a plane symmetry perpendicular to this
axis. The laser’s emission wavelength is determined by the low-lying
vibrational and rotational energy levels of the CO molecule.
2
A major breakthrough for the CO laser came with the improved
2
excitation of the CO molecule by the addition of nitrogen to the
2