Page 455 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 455
422 Fi b er L a s er s Intr oduction to Optical Fiber Lasers 423
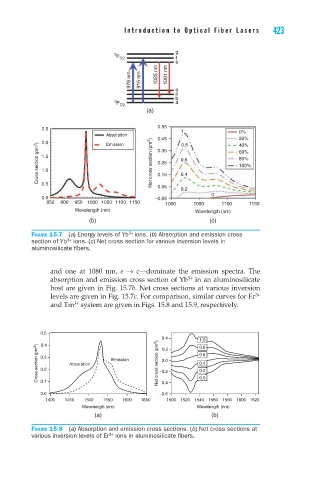
g
3
F 5/2 f
e
976 nm 915 nm 1025 nm 1081 nm
d
c
b
3 a
F
7/2
(a)
0.55
2.5
1 0%
Absorption 0.45 0.8 20%
2.0
Cross section (pm 2 ) 1.5 Net cross section (pm 2 ) 0.35 0.6 60%
Emission
40%
80%
0.25
100%
1.0
0.4
0.15
0.5
0.05
0.2
0
0.0 −0.05
850 900 950 1000 1050 1100 1150 1000 1050 1100 1150
Wavelength (nm) Wavelength (nm)
(b) (c)
3+
Figure 15.7 (a) Energy levels of Yb ions. (b) Absorption and emission cross
3+
section of Yb ions. (c) Net cross section for various inversion levels in
aluminosilicate fibers.
and one at 1080 nm, e → c—dominate the emission spectra. The
3+
absorption and emission cross section of Yb in an aluminosilicate
host are given in Fig. 15.7b. Net cross sections at various inversion
levels are given in Fig. 15.7c. For comparison, similar curves for Er
3+
3+
and Tm system are given in Figs. 15.8 and 15.9, respectively.
0.5
0.4 1.0
0.4
Cross section (pm 2 ) 0.3 Absorption Emission Net cross section (pm 2 ) −0.2 0.6
0.8
0.2
0.0
0.4
0.2
0.2
0.0
0.1
0.0 −0.4
−0.6
1400 1450 1500 1550 1600 1650 1500 1520 1540 1560 1580 1600 1620
Wavelength (nm) Wavelength (nm)
(a) (b)
Figure 15.8 (a) Absorption and emission cross sections. (b) Net cross sections at
various inversion levels of Er ions in aluminosilicate fibers.
3+