Page 43 - How To Solve Word Problems In Calculus
P. 43
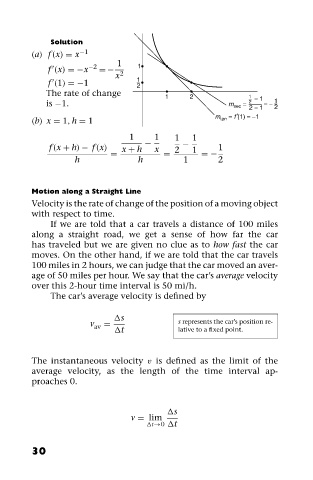
Solution
(a) f (x) = x −1
1
f (x) =−x −2 =− 1
x 2
f (1) =−1 1 2
The rate of change
1 2 1 − 1
is −1. m sec = 2 2 − 1 =− 1
2
m tan = f (1) = −1
(b) x = 1, h = 1
1 1 1 1
f (x + h) − f (x) x + h − x 2 − 1 1
= = =−
h h 1 2
Motion along a Straight Line
Velocity is the rate of change of the position of a moving object
with respect to time.
If we are told that a car travels a distance of 100 miles
along a straight road, we get a sense of how far the car
has traveled but we are given no clue as to how fast the car
moves. On the other hand, if we are told that the car travels
100 miles in 2 hours, we can judge that the car moved an aver-
age of 50 miles per hour. We say that the car’s average velocity
over this 2-hour time interval is 50 mi/h.
The car’s average velocity is defined by
s
v = s represents the car’s position re-
av
t lative to a fixed point.
The instantaneous velocity v is defined as the limit of the
average velocity, as the length of the time interval ap-
proaches 0.
s
v = lim
t→0 t
30