Page 229 - Hydrocarbon
P. 229
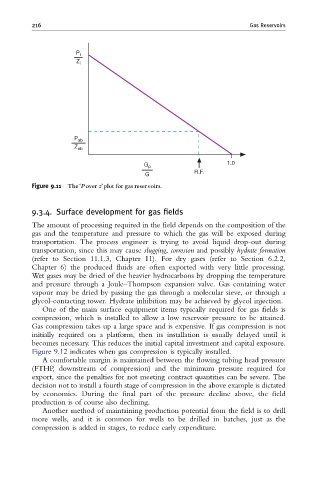
216 Gas Reservoirs
P i
Z i
P ab
Z ab
1.0
G p
R.F.
G
Figure 9.11 The‘P over z’plot for gas reservoirs.
9.3.4. Surface development for gas fields
The amount of processing required in the field depends on the composition of the
gas and the temperature and pressure to which the gas will be exposed during
transportation. The process engineer is trying to avoid liquid drop-out during
transportation, since this may cause slugging, corrosion and possibly hydrate formation
(refer to Section 11.1.3, Chapter 11). For dry gases (refer to Section 6.2.2,
Chapter 6) the produced fluids are often exported with very little processing.
Wet gases may be dried of the heavier hydrocarbons by dropping the temperature
and pressure through a Joule–Thompson expansion valve. Gas containing water
vapour may be dried by passing the gas through a molecular sieve, or through a
glycol-contacting tower. Hydrate inhibition may be achieved by glycol injection.
One of the main surface equipment items typically required for gas fields is
compression, which is installed to allow a low reservoir pressure to be attained.
Gas compression takes up a large space and is expensive. If gas compression is not
initially required on a platform, then its installation is usually delayed until it
becomes necessary. This reduces the initial capital investment and capital exposure.
Figure 9.12 indicates when gas compression is typically installed.
A comfortable margin is maintained between the flowing tubing head pressure
(FTHP, downstream of compression) and the minimum pressure required for
export, since the penalties for not meeting contract quantities can be severe. The
decision not to install a fourth stage of compression in the above example is dictated
by economics. During the final part of the pressure decline above, the field
production is of course also declining.
Another method of maintaining production potential from the field is to drill
more wells, and it is common for wells to be drilled in batches, just as the
compression is added in stages, to reduce early expenditure.