Page 252 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 252
Well Dynamic Behaviour 239
Well
flowrate flowing shut-in
period
period
(b/d)
Time
P i
pressure
Bottom
hole pressure build-up
pressure drawdown
(psig)
Time
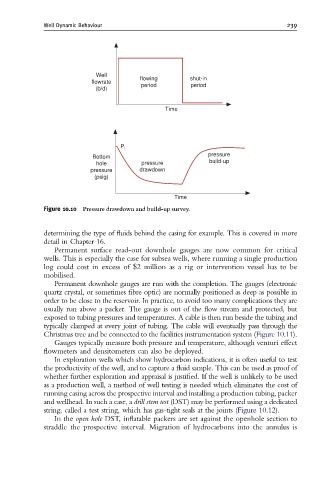
Figure 10.10 Pressure drawdown and build-up survey.
determining the type of fluids behind the casing for example. This is covered in more
detail in Chapter 16.
Permanent surface read-out downhole gauges are now common for critical
wells. This is especially the case for subsea wells, where running a single production
log could cost in excess of $2 million as a rig or intervention vessel has to be
mobilised.
Permanent downhole gauges are run with the completion. The gauges (electronic
quartz crystal, or sometimes fibre optic) are normally positioned as deep as possible in
order to be close to the reservoir. In practice, to avoid too many complications they are
usually run above a packer. The gauge is out of the flow stream and protected, but
exposed to tubing pressures and temperatures. A cable is then run beside the tubing and
typically clamped at every joint of tubing. The cable will eventually pass through the
Christmas tree and be connected to the facilities instrumentation system (Figure 10.11).
Gauges typically measure both pressure and temperature, although venturi effect
flowmeters and densitometers can also be deployed.
In exploration wells which show hydrocarbon indications, it is often useful to test
the productivity of the well, and to capture a fluid sample. This can be used as proof of
whether further exploration and appraisal is justified. If the well is unlikely to be used
as a production well, a method of well testing is needed which eliminates the cost of
running casing across the prospective interval and installing a production tubing, packer
and wellhead. In such a case, a drill stem test (DST) may be performed using a dedicated
string, called a test string, which has gas-tight seals at the joints (Figure 10.12).
In the open hole DST, inflatable packers are set against the openhole section to
straddle the prospective interval. Migration of hydrocarbons into the annulus is