Page 271 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 271
258 Artificial Lift
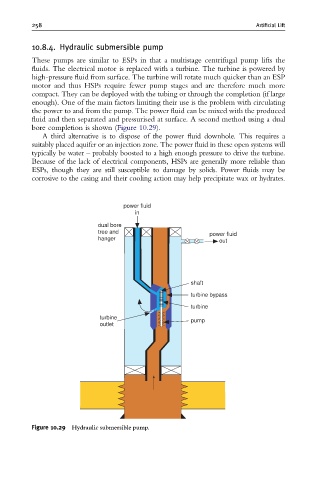
10.8.4. Hydraulic submersible pump
These pumps are similar to ESPs in that a multistage centrifugal pump lifts the
fluids. The electrical motor is replaced with a turbine. The turbine is powered by
high-pressure fluid from surface. The turbine will rotate much quicker than an ESP
motor and thus HSPs require fewer pump stages and are therefore much more
compact. They can be deployed with the tubing or through the completion (if large
enough). One of the main factors limiting their use is the problem with circulating
the power to and from the pump. The power fluid can be mixed with the produced
fluid and then separated and pressurised at surface. A second method using a dual
bore completion is shown (Figure 10.29).
A third alternative is to dispose of the power fluid downhole. This requires a
suitably placed aquifer or an injection zone. The power fluid in these open systems will
typically be water – probably boosted to a high enough pressure to drive the turbine.
Because of the lack of electrical components, HSPs are generally more reliable than
ESPs,though they are still susceptibletodamagebysolids. Powerfluids maybe
corrosive to the casing and their cooling action may help precipitate wax or hydrates.
power fluid
in
dual bore
tree and
power fluid
hanger out
shaft
turbine bypass
turbine
turbine pump
outlet
Figure 10.29 Hydraulic submersible pump.