Page 335 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 335
322 Maintenance Engineering Input to the FDP
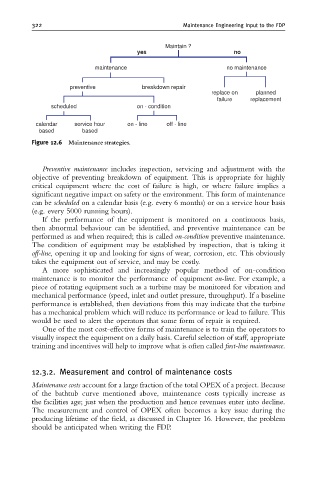
Maintain ?
yes no
maintenance no maintenance
preventive breakdown repair
replace on planned
failure replacement
scheduled on - condition
calendar service hour on - line off - line
based based
Figure 12.6 Maintenance strategies.
Preventive maintenance includes inspection, servicing and adjustment with the
objective of preventing breakdown of equipment. This is appropriate for highly
critical equipment where the cost of failure is high, or where failure implies a
significant negative impact on safety or the environment. This form of maintenance
can be scheduled on a calendar basis (e.g. every 6 months) or on a service hour basis
(e.g. every 5000 running hours).
If the performance of the equipment is monitored on a continuous basis,
then abnormal behaviour can be identified, and preventive maintenance can be
performed as and when required; this is called on-condition preventive maintenance.
The condition of equipment may be established by inspection, that is taking it
off-line, opening it up and looking for signs of wear, corrosion, etc. This obviously
takes the equipment out of service, and may be costly.
A more sophisticated and increasingly popular method of on-condition
maintenance is to monitor the performance of equipment on-line. For example, a
piece of rotating equipment such as a turbine may be monitored for vibration and
mechanical performance (speed, inlet and outlet pressure, throughput). If a baseline
performance is established, then deviations from this may indicate that the turbine
has a mechanical problem which will reduce its performance or lead to failure. This
would be used to alert the operators that some form of repair is required.
One of the most cost-effective forms of maintenance is to train the operators to
visually inspect the equipment on a daily basis. Careful selection of staff, appropriate
training and incentives will help to improve what is often called first-line maintenance.
12.3.2. Measurement and control of maintenance costs
Maintenance costs account for a large fraction of the total OPEX of a project. Because
of the bathtub curve mentioned above, maintenance costs typically increase as
the facilities age; just when the production and hence revenues enter into decline.
The measurement and control of OPEX often becomes a key issue during the
producing lifetime of the field, as discussed in Chapter 16. However, the problem
should be anticipated when writing the FDP.