Page 426 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 426
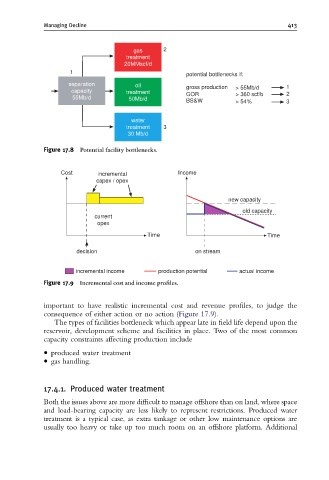
Managing Decline 413
gas 2
treatment
20MMscf/d
1 potential bottlenecks if:
separation oil gross production 1
capacity treatment GOR > 55Mb/d 2
> 360 scf/b
55Mb/d 50Mb/d BS&W > 54% 3
water
treatment 3
30 Mb/d
Figure 17.8 Potential facility bottlenecks.
Cost incremental Income
capex / opex
new capacity
old capacity
current
opex
Time Time
decision on stream
incremental income production potential actual income
Figure 17.9 Incremental cost and income pro¢les.
important to have realistic incremental cost and revenue profiles, to judge the
consequence of either action or no action (Figure 17.9).
The types of facilities bottleneck which appear late in field life depend upon the
reservoir, development scheme and facilities in place. Two of the most common
capacity constraints affecting production include
produced water treatment
gas handling.
17.4.1. Produced water treatment
Both the issues above are more difficult to manage offshore than on land, where space
and load-bearing capacity are less likely to represent restrictions. Produced water
treatment is a typical case, as extra tankage or other low maintenance options are
usually too heavy or take up too much room on an offshore platform. Additional