Page 83 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 83
70 Drilling Techniques
1 2 3 4
1 = on bottom in
oriented position
2 = drilling rathole
3 = whipstock is
removed
4 = opening rathole
to full gauge
with hole opener
Figure 4.21 Kicking o¡ with a whipstock.
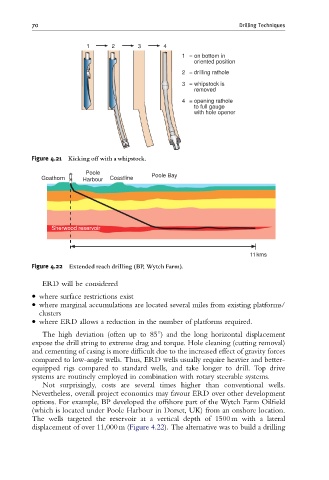
Poole
Goathorn Harbour Coastline Poole Bay
Sherwood reservoir
11 kms
Figure 4.22 Extended reach drilling (BP, Wytch Farm).
ERD will be considered
where surface restrictions exist
where marginal accumulations are located several miles from existing platforms/
clusters
where ERD allows a reduction in the number of platforms required.
The high deviation (often up to 851) and the long horizontal displacement
expose the drill string to extreme drag and torque. Hole cleaning (cutting removal)
and cementing of casing is more difficult due to the increased effect of gravity forces
compared to low-angle wells. Thus, ERD wells usually require heavier and better-
equipped rigs compared to standard wells, and take longer to drill. Top drive
systems are routinely employed in combination with rotary steerable systems.
Not surprisingly, costs are several times higher than conventional wells.
Nevertheless, overall project economics may favour ERD over other development
options. For example, BP developed the offshore part of the Wytch Farm Oilfield
(which is located under Poole Harbour in Dorset, UK) from an onshore location.
The wells targeted the reservoir at a vertical depth of 1500 m with a lateral
displacement of over 11,000 m (Figure 4.22). The alternative was to build a drilling