Page 147 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 147
PHOSPHORIC ACID 147
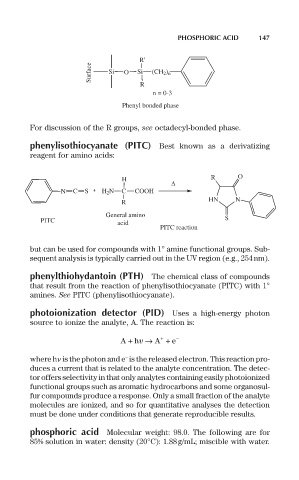
R'
Surface Si O Si (CH 2 ) n
R
n = 0-3
Phenyl bonded phase
For discussion of the R groups, see octadecyl-bonded phase.
phenylisothiocyanate (PITC) Best known as a derivatizing
reagent for amino acids:
H R O
D
N C S + H 2 N C COOH
HN N
R
General amino
PITC acid S
PITC reaction
but can be used for compounds with 1° amine functional groups. Sub-
sequent analysis is typically carried out in the UV region (e.g., 254nm).
phenylthiohydantoin (PTH) The chemical class of compounds
that result from the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate (PITC) with 1°
amines. See PITC (phenylisothiocyanate).
photoionization detector (PID) Uses a high-energy photon
source to ionize the analyte, A. The reaction is:
+
A + h Æ A + e -
v
-
where h is the photon and e is the released electron. This reaction pro-
duces a current that is related to the analyte concentration. The detec-
tor offers selectivity in that only analytes containing easily photoionized
functional groups such as aromatic hydrocarbons and some organosul-
fur compounds produce a response. Only a small fraction of the analyte
molecules are ionized, and so for quantitative analyses the detection
must be done under conditions that generate reproducible results.
phosphoric acid Molecular weight: 98.0. The following are for
85% solution in water: density (20°C): 1.88g/mL; miscible with water.