Page 152 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 152
152 POLYDISPERSITY, M w /M n
N
1)
Cl
Surface Si OH + Cl Si CH 2 (CH 2 ) n CH 3 Surface Si O Si CH 2 (CH 2 ) n CH 3
OH
2) H 2 O
Cl
OH
N
1)
Surface Si O Si CH 2 (CH 2 ) n CH 3Cl Si CH 2 (CH 2 ) n CH 3 Surface Si O Si CH 2 (CH 2 ) n CH 3
OH
Cl
OH
+
2) H 2 O
OH
Cl
O
OH Si CH 2 (CH 2 ) n CH 3
OH
Etc....
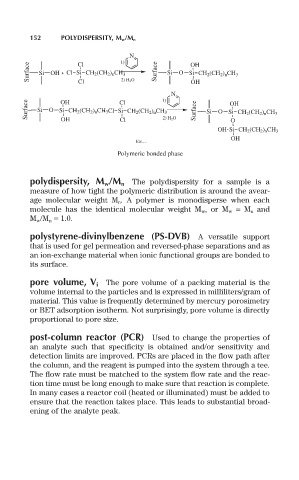
Polymeric bonded phase
polydispersity, M w/M n The polydispersity for a sample is a
measure of how tight the polymeric distribution is around the avear-
age molecular weight M n. A polymer is monodisperse when each
molecule has the identical molecular weight M w, or M w = M n and
M w/M n = 1.0.
polystyrene-divinylbenzene (PS-DVB) A versatile support
that is used for gel permeation and reversed-phase separations and as
an ion-exchange material when ionic functional groups are bonded to
its surface.
pore volume, V i The pore volume of a packing material is the
volume internal to the particles and is expressed in milliliters/gram of
material. This value is frequently determined by mercury porosimetry
or BET adsorption isotherm. Not surprisingly, pore volume is directly
proportional to pore size.
post-column reactor (PCR) Used to change the properties of
an analyte such that specificity is obtained and/or sensitivity and
detection limits are improved. PCRs are placed in the flow path after
the column, and the reagent is pumped into the system through a tee.
The flow rate must be matched to the system flow rate and the reac-
tion time must be long enough to make sure that reaction is complete.
In many cases a reactor coil (heated or illuminated) must be added to
ensure that the reaction takes place. This leads to substantial broad-
ening of the analyte peak.