Page 148 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 148
148 PHOTODIODE-ARRAY DETECTOR (PDA)
H 3 PO 4
Phosphoric acid
The three pK a values are: pK 1: 2.1, pK 2: 7.2, pK 3: 12.3. Phosphoric acid
and its alkali salts (e.g., sodium and potassium) are frequently used
in LC separations as solution buffers. Note, however, that the solu-
bility of phosphate salts in acetonitrile is limited.
photodiode-array detector (PDA) A PDA detector uses a deu-
terium lamp for the UV spectrum and a tungsten lamp for the visible
spectrum. The PDA detector differs from the single-wavelength detec-
tor in that all the source light passes through the sample. Discrete
wavelengths are then generated by a dispersive element (e.g., prism)
that is placed between the sample cell and a series of detector diodes.
Each diode subtends a fixed wavelength range depending on its dis-
tance from the element, the angular position from the element, and
the dispersive power of the element.
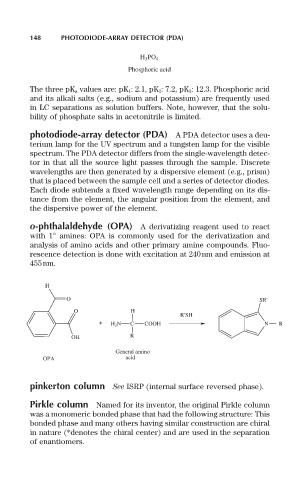
o-phthalaldehyde (OPA) A derivatizing reagent used to react
with 1° amines: OPA is commonly used for the derivatization and
analysis of amino acids and other primary amine compounds. Fluo-
rescence detection is done with excitation at 240nm and emission at
455nm.
H
O SR'
O H
R'SH
+ H 2 N C COOH N R
OH R
General amino
OPA acid
pinkerton column See ISRP (internal surface reversed phase).
Pirkle column Named for its inventor, the original Pirkle column
was a monomeric bonded phase that had the following structure: This
bonded phase and many others having similar construction are chiral
in nature (*denotes the chiral center) and are used in the separation
of enantiomers.