Page 60 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 60
DIOL BONDED PHASE 55
dimethyl formamide (DMF) Molecular weight: 73.1; boiling
point: 153°C; refractive index (20°C): 1.4305; density (20°C): 0.95g/mL;
viscosity (20°C): 0.92cP; UV cutoff: 268nm; polarity index (P¢): 6.4;
Hildebrand solubility parameter (d): 11.5. Miscible with water. Com-
bustible. Dimethyl formamide is a rarely used solvent in HPLC and
GPC.
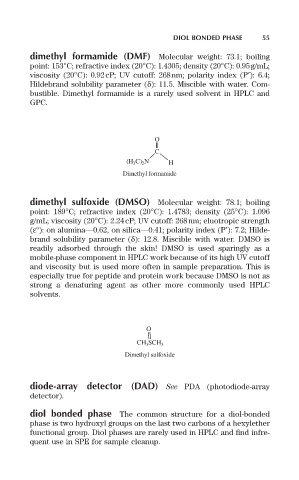
O
C
(H 3 C) 2 N H
Dimethyl formamide
dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) Molecular weight: 78.1; boiling
point: 189°C; refractive index (20°C): 1.4783; density (25°C): 1.096
g/mL; viscosity (20°C): 2.24cP; UV cutoff: 268nm; eluotropic strength
o
(e ): on alumina—0.62, on silica—0.41; polarity index (P¢): 7.2; Hilde-
brand solubility parameter (d): 12.8. Miscible with water. DMSO is
readily adsorbed through the skin! DMSO is used sparingly as a
mobile-phase component in HPLC work because of its high UV cutoff
and viscosity but is used more often in sample preparation. This is
especially true for peptide and protein work because DMSO is not as
strong a denaturing agent as other more commonly used HPLC
solvents.
O
CH 3 SCH 3
Dimethyl sulfoxide
diode-array detector (DAD) See PDA (photodiode-array
detector).
diol bonded phase The common structure for a diol-bonded
phase is two hydroxyl groups on the last two carbons of a hexylether
functional group. Diol phases are rarely used in HPLC and find infre-
quent use in SPE for sample cleanup.