Page 55 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 55
50 DARCY’S LAW
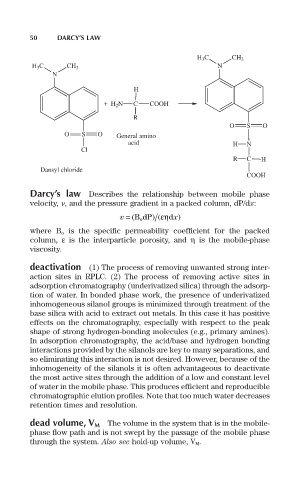
H 3 C CH 3
H 3 C CH 3 N
N
H
+ H 2 N C COOH
R
O S O
O S O General amino
acid H N
Cl
R C H
Dansyl chloride
COOH
Darcy’s law Describes the relationship between mobile phase
velocity, , and the pressure gradient in a packed column, dP/dx:
v = (BdP ) (eh d x)
o
where B o is the specific permeability coefficient for the packed
column, e is the interparticle porosity, and h is the mobile-phase
viscosity.
deactivation (1) The process of removing unwanted strong inter-
action sites in RPLC. (2) The process of removing active sites in
adsorption chromatography (underivatized silica) through the adsorp-
tion of water. In bonded phase work, the presence of underivatized
inhomogeneous silanol groups is minimized through treatment of the
base silica with acid to extract out metals. In this case it has positive
effects on the chromatography, especially with respect to the peak
shape of strong hydrogen-bonding molecules (e.g., primary amines).
In adsorption chromatography, the acid/base and hydrogen bonding
interactions provided by the silanols are key to many separations, and
so eliminating this interaction is not desired. However, because of the
inhomogeneity of the silanols it is often advantageous to deactivate
the most active sites through the addition of a low and constant level
of water in the mobile phase. This produces efficient and reproducible
chromatographic elution profiles. Note that too much water decreases
retention times and resolution.
The volume in the system that is in the mobile-
dead volume, V M
phase flow path and is not swept by the passage of the mobile phase
through the system. Also see hold-up volume, V M.