Page 52 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 52
CYCLOHEXANE 47
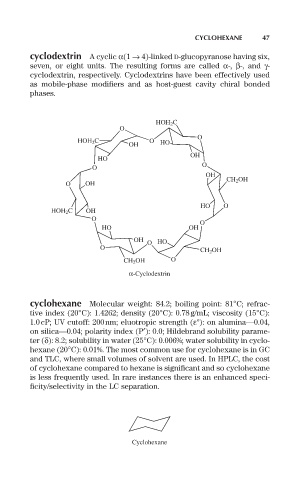
cyclodextrin A cyclic a(1 Æ 4)-linked D-glucopyranose having six,
seven, or eight units. The resulting forms are called a-, b-, and g-
cyclodextrin, respectively. Cyclodextrins have been effectively used
as mobile-phase modifiers and as host-guest cavity chiral bonded
phases.
HOH 2 C
O
O
HOH 2 C O HO
OH
OH
HO
O
O
OH
CH 2 OH
O OH
HO O
HOH 2 C OH
O
O
HO OH
OH O HO
O CH 2 OH
CH 2 OH O
a-Cyclodextrin
cyclohexane Molecular weight: 84.2; boiling point: 81°C; refrac-
tive index (20°C): 1.4262; density (20°C): 0.78g/mL; viscosity (15°C):
o
1.0cP; UV cutoff: 200nm; eluotropic strength (e ): on alumina—0.04,
on silica—0.04; polarity index (P¢): 0.0; Hildebrand solubility parame-
ter (d): 8.2; solubility in water (25°C): 0.006%; water solubility in cyclo-
hexane (20°C): 0.01%. The most common use for cyclohexane is in GC
and TLC, where small volumes of solvent are used. In HPLC, the cost
of cyclohexane compared to hexane is significant and so cyclohexane
is less frequently used. In rare instances there is an enhanced speci-
ficity/selectivity in the LC separation.
Cyclohexane