Page 70 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 70
66 ELUTION VOLUME, V R
elution volume, V R The volume of the mobile phase required to
elute an analyte from the column, calculated as:
V R = F ¥ t r
where F is the flow rate and t r is the retention time at the peak
maximum.
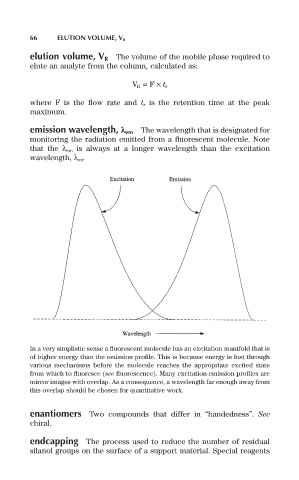
emission wavelength, l em The wavelength that is designated for
monitoring the radiation emitted from a fluorescent molecule. Note
that the l em is always at a longer wavelength than the excitation
wavelength, l ex.
In a very simplistic sense a fluorescent molecule has an excitation manifold that is
of higher energy than the emission profile. This is because energy is lost through
various mechanisms before the molecule reaches the appropriate excited state
from which to fluoresce (see fluorescence). Many excitation-emission profiles are
mirror images with overlap. As a consequence, a wavelength far enough away from
this overlap should be chosen for quantitative work.
enantiomers Two compounds that differ in “handedness”. See
chiral.
endcapping The process used to reduce the number of residual
silanol groups on the surface of a support material. Special reagents