Page 176 - Improving Machinery Reliability
P. 176
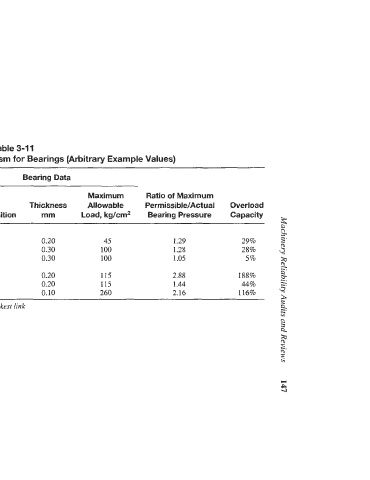
Table 3-1 1
Determination of Design Conservatism for Bearings (Arbitrary Example Values)
Bearing Data
Maximum Ratio of Maximum
Projected Actual Bearing Thickness Allowable Permissible/Actual Overload
Area cm2 Pressure kg/cm2 Composition mm Load, kg/cm2 Bearing Pressure Capacity
3
Vendor X 3
5
Main Bearing 1,900 35 tI 0.20 45 1.29 29% m
Crank Bearing 1,700 78 I1 0.30 100 1.28 28% 9
Crosshead Bearing 1,400 95 I1 0.30 100 1.05 5%
Vendor Y !?
fi'
z
Main Bearing 1,800 40 I1 0.20 115 2.88 188% -
Crank Bearing 1,800 80 I1 0.20 115 1.44 44%
Crosshead Bearing 1,200 120 I 0.10 260 2.16 116%
r:
Resulr: Overload Capacity Vendor X = 5%. Crosshead bearings are the weakest link a. -_
Overload Capacity Vendor Y = 44%. Crank bearings are the weakesr link 2
a
3
a.