Page 103 - Industrial Cutting of Textile Materials
P. 103
90 Industrial Cutting of Textile Materials
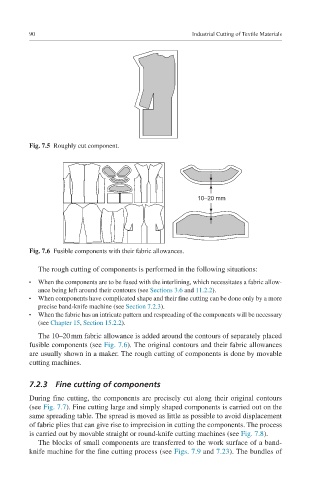
Fig. 7.5 Roughly cut component.
10–20 mm
Fig. 7.6 Fusible components with their fabric allowances.
The rough cutting of components is performed in the following situations:
When the components are to be fused with the interlining, which necessitates a fabric allow-
●
ance being left around their contours (see Sections 3.6 and 11.2.2).
When components have complicated shape and their fine cutting can be done only by a more
●
precise band-knife machine (see Section 7.2.3).
When the fabric has an intricate pattern and respreading of the components will be necessary
●
(see Chapter 15, Section 15.2.2).
The 10–20 mm fabric allowance is added around the contours of separately placed
fusible components (see Fig. 7.6). The original contours and their fabric allowances
are usually shown in a maker. The rough cutting of components is done by movable
cutting machines.
7.2.3 Fine cutting of components
During fine cutting, the components are precisely cut along their original contours
(see Fig. 7.7). Fine cutting large and simply shaped components is carried out on the
same spreading table. The spread is moved as little as possible to avoid displacement
of fabric plies that can give rise to imprecision in cutting the components. The process
is carried out by movable straight or round-knife cutting machines (see Fig. 7.8).
The blocks of small components are transferred to the work surface of a band-
knife machine for the fine cutting process (see Figs. 7.9 and 7.23). The bundles of