Page 235 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 235
8/21 4 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
Force
Force
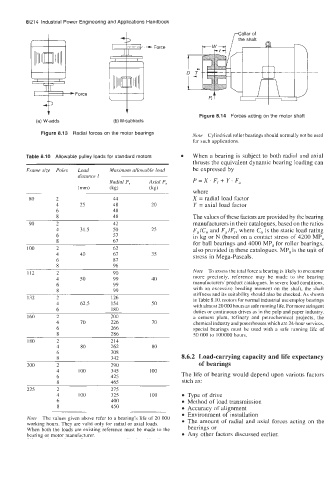
Figure 8.14 Forces acting on the motor shaft
(a) W-adds (b) W-subtracts
Figure 8.13 Radial forces on the motor bearings Note Cylindrical roller bearings should normally not be used
for such applications.
Table 8.10 Allowable pulley loads for standard motors When a bearing is subject to both radial and axial
thrusts the equivalent dynamic bearing loading can
Frame size Poles Load Maximum allowable load be expressed by
distance 1
Radial P, Axial Pa P=X. F,+ Y. Fa
(mm) (k&) (k&)
where
80 2 44 X = radial load factor
4 25 48 20 Y = axial load factor
6 48
8 48 The values of these factors are provided by the bearing
90 2 42 manufacturers in their catalogues, based on the ratios
4 31.5 50 25 F,IC, and F, IFr, where C, is the static load rating
6 51 in kg or N (based on a contact stress of 4200 MP,
8 67 for ball bearings and 4000 MP, for roller bearings,
100 2 62 also provided in these catalogues. MP, is the unit of
4 40 67 35 stress in Mega-Pascals.
6 87
8 96
112 2 90 Note To assess the total force a bearing is likely to encounter
4 50 99 40 more precisely, reference may be made to the bearing
6 99 manufacturers’ product catalogues. In severe load conditions,
8 99 with an excessive bending moment on the shaft, the shaft
132 2 126 stiffness and its suitability should also be checked. As shown
in Table 8.10, motors for normal industrial use employ bearings
4 62.5 154 50 with almost 20 000 hours as safe running life. For more stringent
6 1 xn duties or continuous drives as in the pulp and paper industry,
160 2 200 a cement plant, refinery and petrochemical projects, the
4 70 226 70 chemical industry and powerhouses which are 24-hour services,
6 266 special bearings must be used with a safe running life of
8 286 50 000 to 100000 hours.
180 2 214
4 80 262 80
6 308
8 342 8.6.2 Load-carrying capacity and life expectancy
200 2 290 of bearings
4 100 345 100
6 425 The life of bearing would depend upon various factors
8 465 such as:
225 2 275
4 100 325 100 Type of drive
6 400 Method of load transmission
8 450 Accuracy of alignment
Environment of installation
Note The values given above refer to a bearing’s life of 20 000 The amount of radial and axial forces acting on the
working hours. They are valid only for radial or axial loads.
When both the loads are existing reference must be made to the bearings or
bearing or motor manufacturer. Any other factors discussed earlier.