Page 434 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 434
13/408 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
process), which a regular production line can ill
afford.
They would require a larger storage area, which
should be dustproof but well ventilated to provide
for sufficient air circulation.
During the drying time, the workpiece may collect
dust from suspended dust particles in the atmosphere.
The air dried surfaces may not be as neat and hard
as the stoved surfaces. Door
6 Stove curing is a rapid method and is obtained by
baking the paint for a specific time in a furnace at a
specific temperature. The temperature and time will
depend upon the type of paint being used and its
thickness, the shape of the workpiece and the
effectiveness of the furnace. (Refer to Table A13.4.)
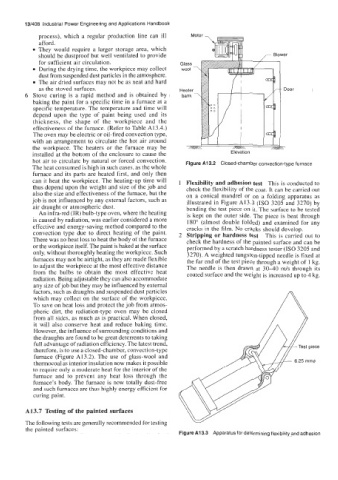
The oven may be electric or oil-fired convection type,
with an arrangement to circulate the hot air around
the workpiece. The heaters or the furnace may be -
installed at the bottom of the enclosure to cause the
hot air to circulate by natural or forced convection.
The heat consumed is high in such cases, as the whole Figure A13.2 Closed-chamber convection-type furnace
furnace and its parts are heated first, and only then
can it heat the workpiece. The heating-up time will 1 Flexibility and adhesion test This is conducted to
thus depend upon the weight and size of the job and check the flexibility of the coat. It can be carried out
also the size and effectiveness of the furnace, but the on a conical mandrel or on a folding apparatus as
job is not influenced by any external factors, such as illustrated in Figure A13.3 (IS0 3205 and 3270) by
air draught or atmospheric dust. bending the test piece on it. The surface to be tested
An infra-red (IR) bulb-type oven, where the heating is kept on the outer side. The piece is bent through
is caused by radiation, was earlier considered a more 180" (almost double folded) and examined for any
effective and energy-saving method compared to the cracks in the film. No cracks should develop.
convection type due to direct heating of the paint. 2 Stripping or hardness test This is carried out to
There was no heat loss to heat the body of the furnace check the hardness of the painted surface and can be
or the workpiece itself. The paint is baked at the surface performed by a scratch hardness tester (IS0 3205 and
only, without thoroughly heating the workpiece. Such 3270). A weighted tungsten-tipped needle is fixed at
furnaces may not be airtight, as they are made flexible the far end of the test piece through a weight of 1 kg.
to adjust the workpiece at the most effective distance The needle is then drawn at 30-40 m/s through its
from the bulbs to obtain the most effective heat coated surface and the weight is increased up to 4 kg.
radiation. Being adjustable they can also accommodate
any size of job but they may be influenced by external
factors, such as draughts and suspended dust particles
which may collect on the surface of the workpiece.
To save on heat loss and protect the job from atmos-
pheric dirt, the radiation-type oven may be closed
from all sides, as much as is practical. When closed,
it will also conserve heat and reduce baking time.
However, the influence of surrounding conditions and
the draughts are found to be great deterrents to taking
full advantage of radiation efficiency. The latest trend,
therefore, is to use a closed-chamber, convection-type
furnace (Figure A13.2). The use of glass-wool and
thermocoal as interior insulation now makes it possible
to require only a moderate heat for the interior of the
furnace and to prevent any heat loss through the
furnace's body. The furnace is now totally dust-free
and such furnaces are thus highly energy efficient for
curing paint.
A13.7 Testing of the painted surfaces
The following tests are generally recommended for testing
the painted surfaces:
Figure A13.3 Apparatus for determining flexibility and adhesion