Page 313 - Industrial Ventilation Design Guidebook
P. 313
5.3 TOXICITY AND RISKS INDUCED BY OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 269
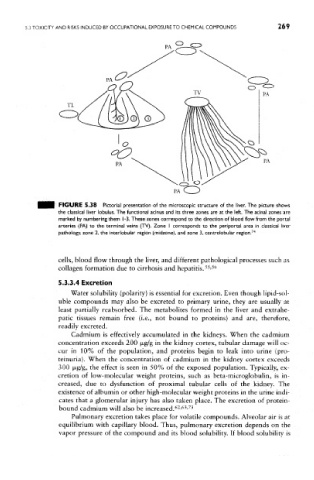
FIGURE 5.38 Pictorial presentation of the microscopic structure of the liver. The picture shows
the classical liver lobulus. The functional acinus and its three zones are at the left. The acina! zones are
marked by numbering them 1-3. These zones correspond to the direction of blood flow from the portal
arteries (PA) to the terminal veins (TV). Zone I corresponds to the periportal area in classical liver
pathology, zone 2, the interlobular region (midzone), and zone 3, centrelobular region. 74
cells, blood flow through the liver, and different pathological processes such as
55 56
collagen formation due to cirrhosis and hepatitis. '
5.3.3.4 Excretion
Water solubility (polarity) is essential for excretion. Even though lipid-sol-
uble compounds may also be excreted to primary urine, they are usually at
least partially reabsorbed. The metabolites formed in the liver and extrahe-
patic tissues remain free (i.e., not bound to proteins) and are, therefore,
readily excreted.
Cadmium is effectively accumulated in the kidneys. When the cadmium
concentration exceeds 200 jxg/g in the kidney cortex, tubular damage will oc-
cur in 10% of the population, and proteins begin to leak into urine (pro-
teinuria). When the concentration of cadmium in the kidney cortex exceeds
300 jxg/g, the effect is seen in 50% of the exposed population. Typically, ex-
cretion of low-molecular weight proteins, such as beta-microglobulin, is in-
creased, due to dysfunction of proximal tubular cells of the kidney. The
existence of albumin or other high-molecular weight proteins in the urine indi-
cates that a glomerular injury has also taken place. The excretion of protein-
62 63 73
bound cadmium will also be increased. ' '
Pulmonary excretion takes place for volatile compounds. Alveolar air is at
equilibrium with capillary blood. Thus, pulmonary excretion depends on the
vapor pressure of the compound and its blood solubility. If blood solubility is