Page 325 - Industrial Ventilation Design Guidebook
P. 325
5.3 TOXIC1TY AND RISKS INDUCED BY OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 28 I
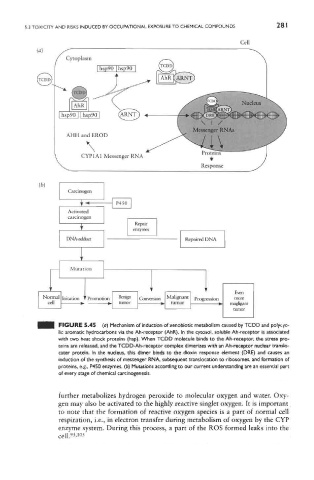
FIGURE 5.45 (a) Mechanism of induction of xenobiotic metabolism caused by TCDD and polyc/c-
lic aromatic hydrocarbons via the Ah-receptor (AhR). In the cytosol, soluble Ah-receptor is associated
with two heat shock proteins (hsp). When TCDD molecule binds to the Ah-receptor, the stress pro-
teins are released, and the TCDD-Ah-receptor complex dimerizes with an Ah-receptor nuclear translo-
cater protein. In the nucleus, this dimer binds to the dioxin response element (DRE) and causes an
induction of the synthesis of messenger RNA, subsequent translocation to ribosomes, and formation of
proteins, e.g., P450 enzymes, (b) Mutations according to our current understanding are an essential part
of every stage of chemical carcinogenesis.
further metabolizes hydrogen peroxide to molecular oxygen and water. Oxy-
gen may also be activated to the highly reactive singlet oxygen. It is important
to note that the formation of reactive oxygen species is a part of normal cell
respiration, i.e., in electron transfer during metabolism of oxygen by the CYP
enzyme system. During this process, a part of the ROS formed leaks into the
93 105
cell. '