Page 131 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 131
Advanced Physico-chemical Methods of Treatment for Industrial Wastewaters 105
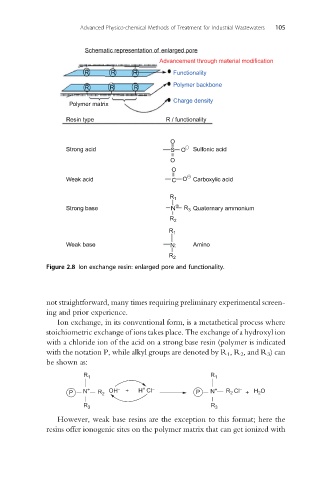
Schematic representation of enlarged pore
Advancement through material modification
R R R Functionality
Polymer backbone
R R R
Charge density
Polymer matrix
Resin type R / functionality
O
Strong acid S O Sulfonic acid
O
O
Weak acid C O Carboxylic acid
R 1
Å
Strong base N R 3 Quaternary ammonium
R 2
R 1
Weak base N: Amino
R 2
Figure 2.8 Ion exchange resin: enlarged pore and functionality.
not straightforward, many times requiring preliminary experimental screen-
ing and prior experience.
Ion exchange, in its conventional form, is a metathetical process where
stoichiometric exchange of ions takes place. The exchange of a hydroxyl ion
with a chloride ion of the acid on a strong base resin (polymer is indicated
with the notation P, while alkyl groups are denoted by R 1 ,R 2 , and R 3 ) can
be shown as:
R 1 R 1
+
P N + R 2 OH − + H Cl − P N + R 2 Cl − + H O
2
R 3 R 3
However, weak base resins are the exception to this format; here the
resins offer ionogenic sites on the polymer matrix that can get ionized with