Page 139 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 139
Advanced Physico-chemical Methods of Treatment for Industrial Wastewaters 113
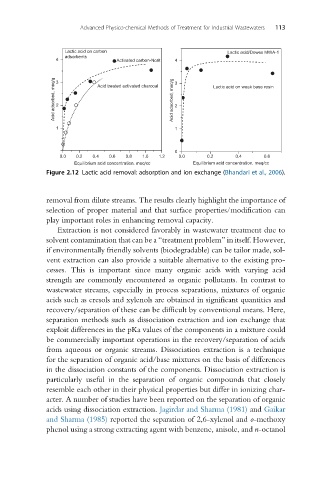
Lactic acid on carbon Lactic acid/Dowex MWA-1
adsorbents
4 Activated carbon-Norit 4
Acid adsorbed, meq/g 3 2 Acid treated activated charcoal Acid adsorbed, meq/g 3 2 Lactic acid on weak base resin
1 1
0
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6
Equilibrium acid concentration. meq/cc Equilibrium acid concentration. meq/cc
Figure 2.12 Lactic acid removal: adsorption and ion exchange (Bhandari et al., 2006).
removal from dilute streams. The results clearly highlight the importance of
selection of proper material and that surface properties/modification can
play important roles in enhancing removal capacity.
Extraction is not considered favorably in wastewater treatment due to
solvent contamination that can be a “treatment problem” in itself. However,
if environmentally friendly solvents (biodegradable) can be tailor made, sol-
vent extraction can also provide a suitable alternative to the existing pro-
cesses. This is important since many organic acids with varying acid
strength are commonly encountered as organic pollutants. In contrast to
wastewater streams, especially in process separations, mixtures of organic
acids such as cresols and xylenols are obtained in significant quantities and
recovery/separation of these can be difficult by conventional means. Here,
separation methods such as dissociation extraction and ion exchange that
exploit differences in the pKa values of the components in a mixture could
be commercially important operations in the recovery/separation of acids
from aqueous or organic streams. Dissociation extraction is a technique
for the separation of organic acid/base mixtures on the basis of differences
in the dissociation constants of the components. Dissociation extraction is
particularly useful in the separation of organic compounds that closely
resemble each other in their physical properties but differ in ionizing char-
acter. A number of studies have been reported on the separation of organic
acids using dissociation extraction. Jagirdar and Sharma (1981) and Gaikar
and Sharma (1985) reported the separation of 2,6-xylenol and o-methoxy
phenol using a strong extracting agent with benzene, anisole, and n-octanol