Page 138 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 138
112 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
of wastewater treatment. The separation of lactic acid/lactate salt can be
accomplished mainly using solvent extraction, ion exchange, adsorption,
distillation, and membrane separation (Scholler et al., 1993; Aljundi et al.,
2005; Schlosser et al., 2005; Lee and Kim, 2011). Joglekar et al. (2006) have
recently reviewed these different methods for the removal of lactic acid and
have confirmed that the uptake of lactic acid for sorption by Dowex
MWA-1 is much higher than that for extraction by Alamine 336. The main
limitation of the method of solvent extraction is in the form of the toxicity of
the solvent, especially with respect to microorganisms apart from solvent
losses due to miscibility of the two phases and operating problems. Adsorp-
tion studies using silicalite molecular sieves were reported recently by
Aljundi et al. (2005). However, their capacities were very low—of the order
of 55 g/kg adsorbent as compared to the typical capacity of 210 g/kg in the
ion exchange resin Amberlite IRA-35. Sorption capacity with commercial
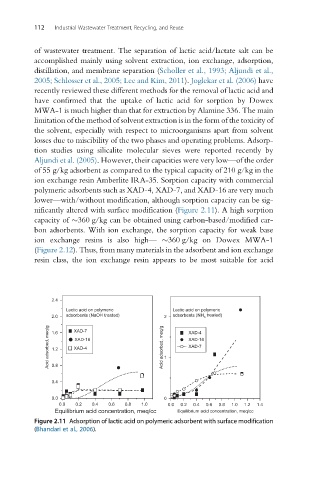
polymeric adsorbents such as XAD-4, XAD-7, and XAD-16 are very much
lower—with/without modification, although sorption capacity can be sig-
nificantly altered with surface modification (Figure 2.11). A high sorption
capacity of 360 g/kg can be obtained using carbon-based/modified car-
bon adsorbents. With ion exchange, the sorption capacity for weak base
ion exchange resins is also high— 360 g/kg on Dowex MWA-1
(Figure 2.12). Thus, from many materials in the adsorbent and ion exchange
resin class, the ion exchange resin appears to be most suitable for acid
2.4
Lactic acid on polymeric Lactic acid on polymeric
2.0 adsorbents (NaOH treated) 2 adsorbents (NH treated)
3
Acid adsorbed, meq/g 1.6 XAD-4 Acid adsorbed, meq/g 1 XAD-4
XAD-7
XAD-16
XAD-16
XAD-7
1.2
0.8
0.4
0.0 0
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4
Equilibrium acid concentration, meq/cc Equilibrium acid concentration, meq/cc
Figure 2.11 Adsorption of lactic acid on polymeric adsorbent with surface modification
(Bhandari et al., 2006).