Page 284 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 284
258 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
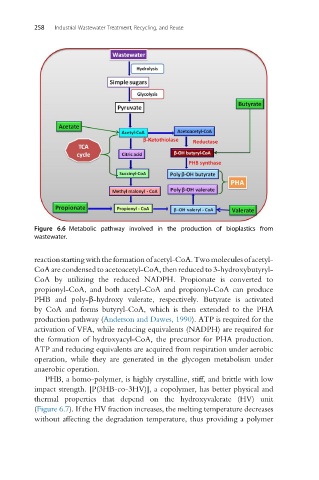
Figure 6.6 Metabolic pathway involved in the production of bioplastics from
wastewater.
reaction starting with the formation of acetyl-CoA.Two molecules of acetyl-
CoA are condensed to acetoacetyl-CoA, then reduced to 3-hydroxybutyryl-
CoA by utilizing the reduced NADPH. Propionate is converted to
propionyl-CoA, and both acetyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA can produce
PHB and poly-b-hydroxy valerate, respectively. Butyrate is activated
by CoA and forms butyryl-CoA, which is then extended to the PHA
production pathway (Anderson and Dawes, 1990). ATP is required for the
activation of VFA, while reducing equivalents (NADPH) are required for
the formation of hydroxyacyl-CoA, the precursor for PHA production.
ATP and reducing equivalents are acquired from respiration under aerobic
operation, while they are generated in the glycogen metabolism under
anaerobic operation.
PHB, a homo-polymer, is highly crystalline, stiff, and brittle with low
impact strength. [P(3HB-co-3HV)], a copolymer, has better physical and
thermal properties that depend on the hydroxyvalerate (HV) unit
(Figure 6.7). If the HV fraction increases, the melting temperature decreases
without affecting the degradation temperature, thus providing a polymer