Page 385 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 385
Phenolic Wastewater Treatment: Development and Applications of New Adsorbent Materials 357
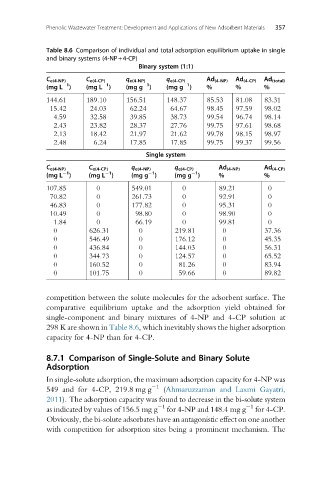
Table 8.6 Comparison of individual and total adsorption equilibrium uptake in single
and binary systems (4-NP+4-CP)
Binary system (1:1)
C e(4-NP) C e(4-CP) q e(4-NP) q e(4-CP) Ad (4-NP) Ad (4-CP) Ad (total)
1
1
1
1
(mg L ) (mg L ) (mg g ) (mg g ) % % %
144.61 189.10 156.51 148.37 85.53 81.08 83.31
15.42 24.03 62.24 64.67 98.45 97.59 98.02
4.59 32.58 39.85 38.73 99.54 96.74 98.14
2.43 23.82 28.37 27.76 99.75 97.61 98.68
2.13 18.42 21.97 21.62 99.78 98.15 98.97
2.48 6.24 17.85 17.85 99.75 99.37 99.56
Single system
C e(4-NP) C e(4-CP) q e(4-NP) q e(4-CP) Ad (4-NP) Ad (4-CP)
1
1
1
1
(mg L ) (mg L ) (mg g ) (mg g ) % %
107.85 0 549.01 0 89.21 0
70.82 0 261.73 0 92.91 0
46.83 0 177.82 0 95.31 0
10.49 0 98.80 0 98.90 0
1.84 0 66.19 0 99.81 0
0 626.31 0 219.81 0 37.36
0 546.49 0 176.12 0 45.35
0 436.84 0 144.03 0 56.31
0 344.73 0 124.57 0 65.52
0 160.52 0 81.26 0 83.94
0 101.75 0 59.66 0 89.82
competition between the solute molecules for the adsorbent surface. The
comparative equilibrium uptake and the adsorption yield obtained for
single-component and binary mixtures of 4-NP and 4-CP solution at
298 K are shown in Table 8.6, which inevitably shows the higher adsorption
capacity for 4-NP than for 4-CP.
8.7.1 Comparison of Single-Solute and Binary Solute
Adsorption
In single-solute adsorption, the maximum adsorption capacity for 4-NP was
1
549 and for 4-CP, 219.8 mg g (Ahmaruzzaman and Laxmi Gayatri,
2011). The adsorption capacity was found to decrease in the bi-solute system
1 1
as indicated by values of 156.5 mg g for 4-NP and 148.4 mg g for 4-CP.
Obviously, the bi-solute adsorbates have an antagonistic effect on one another
with competition for adsorption sites being a prominent mechanism. The