Page 388 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 388
360 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
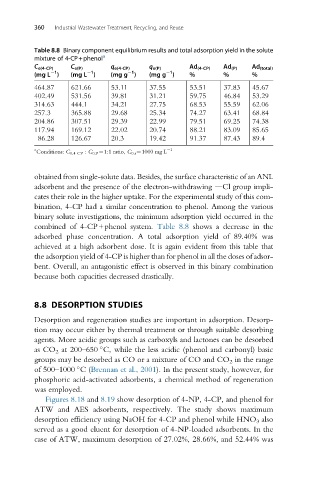
Table 8.8 Binary component equilibrium results and total adsorption yield in the solute
mixture of 4-CP+phenol a
C e(4-CP) C e(P) q e(4-CP) q e(P) Ad (4-CP) Ad (P) Ad (total)
1
1
1
1
(mg L ) (mg L ) (mg g ) (mg g ) % % %
464.87 621.66 53.11 37.55 53.51 37.83 45.67
402.49 531.56 39.81 31.21 59.75 46.84 53.29
314.63 444.1 34.21 27.75 68.53 55.59 62.06
257.3 365.88 29.68 25.34 74.27 63.41 68.84
204.86 307.51 29.39 22.99 79.51 69.25 74.38
117.94 169.12 22.02 20.74 88.21 83.09 85.65
86.28 126.67 20.3 19.42 91.37 87.43 89.4
a 1
Conditions: C 0,4-CP : C 0,P ¼1:1 ratio, C 0,i ¼1000 mg L
obtained from single-solute data. Besides, the surface characteristic of an ANL
adsorbent and the presence of the electron-withdrawing dCl group impli-
cates their role in the higher uptake. For the experimental study of this com-
bination, 4-CP had a similar concentration to phenol. Among the various
binary solute investigations, the minimum adsorption yield occurred in the
combined of 4-CP+phenol system. Table 8.8 shows a decrease in the
adsorbed phase concentration. A total adsorption yield of 89.40% was
achieved at a high adsorbent dose. It is again evident from this table that
the adsorption yield of 4-CP is higher than for phenol in all the doses of adsor-
bent. Overall, an antagonistic effect is observed in this binary combination
because both capacities decreased drastically.
8.8 DESORPTION STUDIES
Desorption and regeneration studies are important in adsorption. Desorp-
tion may occur either by thermal treatment or through suitable desorbing
agents. More acidic groups such as carboxyls and lactones can be desorbed
as CO 2 at 200–650 C, while the less acidic (phenol and carbonyl) basic
groups may be desorbed as CO or a mixture of CO and CO 2 in the range
of 500–1000 C(Brennan et al., 2001). In the present study, however, for
phosphoric acid-activated adsorbents, a chemical method of regeneration
was employed.
Figures 8.18 and 8.19 show desorption of 4-NP, 4-CP, and phenol for
ATW and AES adsorbents, respectively. The study shows maximum
desorption efficiency using NaOH for 4-CP and phenol while HNO 3 also
served as a good eluent for desorption of 4-NP-loaded adsorbents. In the
case of ATW, maximum desorption of 27.02%, 28.66%, and 52.44% was