Page 499 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 499
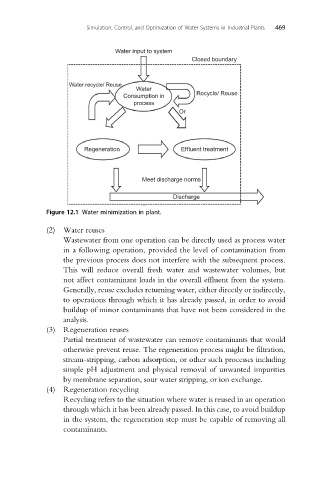
Simulation, Control, and Optimization of Water Systems in Industrial Plants 469
Water input to system
Closed boundary
Water recycle/ Reuse
Water
Consumption in Recycle/ Reuse
process
Or
Regeneration Effluent treatment
Meet discharge norms
Discharge
Figure 12.1 Water minimization in plant.
(2) Water reuses
Wastewater from one operation can be directly used as process water
in a following operation, provided the level of contamination from
the previous process does not interfere with the subsequent process.
This will reduce overall fresh water and wastewater volumes, but
not affect contaminant loads in the overall effluent from the system.
Generally, reuse excludes returning water, either directly or indirectly,
to operations through which it has already passed, in order to avoid
buildup of minor contaminants that have not been considered in the
analysis.
(3) Regeneration reuses
Partial treatment of wastewater can remove contaminants that would
otherwise prevent reuse. The regeneration process might be filtration,
stream-stripping, carbon adsorption, or other such processes including
simple pH adjustment and physical removal of unwanted impurities
by membrane separation, sour water stripping, or ion exchange.
(4) Regeneration recycling
Recycling refers to the situation where water is reused in an operation
through which it has been already passed. In this case, to avoid buildup
in the system, the regeneration step must be capable of removing all
contaminants.