Page 504 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 504
474 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
H S NH 3
2
S
S t
t r
r
Feed i i
p p p
p e
e r
r
Water
Ammonia
S
H 2 NH 3
Feed
Stripper Stripper
Water
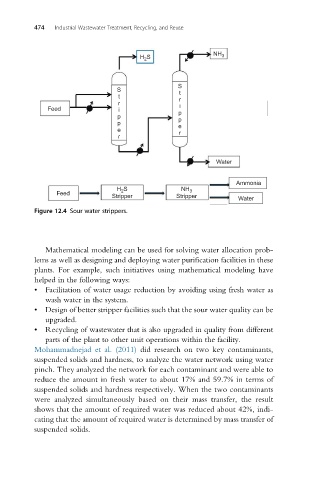
Figure 12.4 Sour water strippers.
Mathematical modeling can be used for solving water allocation prob-
lems as well as designing and deploying water purification facilities in these
plants. For example, such initiatives using mathematical modeling have
helped in the following ways:
• Facilitation of water usage reduction by avoiding using fresh water as
wash water in the system.
• Design of better stripper facilities such that the sour water quality can be
upgraded.
• Recycling of wastewater that is also upgraded in quality from different
parts of the plant to other unit operations within the facility.
Mohammadnejad et al. (2011) did research on two key contaminants,
suspended solids and hardness, to analyze the water network using water
pinch. They analyzed the network for each contaminant and were able to
reduce the amount in fresh water to about 17% and 59.7% in terms of
suspended solids and hardness respectively. When the two contaminants
were analyzed simultaneously based on their mass transfer, the result
shows that the amount of required water was reduced about 42%, indi-
cating that the amount of required water is determined by mass transfer of
suspended solids.