Page 542 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 542
512 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
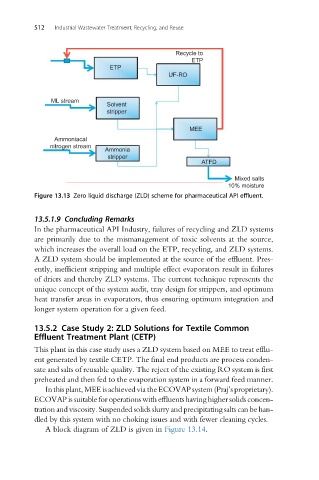
Recycle to
ETP
ETP
UF-RO
ML stream
Solvent
stripper
MEE
Ammoniacal
nitrogen stream
Ammonia
stripper
ATFD
Mixed salts
10% moisture
Figure 13.13 Zero liquid discharge (ZLD) scheme for pharmaceutical API effluent.
13.5.1.9 Concluding Remarks
In the pharmaceutical API Industry, failures of recycling and ZLD systems
are primarily due to the mismanagement of toxic solvents at the source,
which increases the overall load on the ETP, recycling, and ZLD systems.
A ZLD system should be implemented at the source of the effluent. Pres-
ently, inefficient stripping and multiple effect evaporators result in failures
of driers and thereby ZLD systems. The current technique represents the
unique concept of the system audit, tray design for strippers, and optimum
heat transfer areas in evaporators, thus ensuring optimum integration and
longer system operation for a given feed.
13.5.2 Case Study 2: ZLD Solutions for Textile Common
Effluent Treatment Plant (CETP)
This plant in this case study uses a ZLD system based on MEE to treat efflu-
ent generated by textile CETP. The final end products are process conden-
sate and salts of reusable quality. The reject of the existing RO system is first
preheated and then fed to the evaporation system in a forward feed manner.
In thisplant, MEE is achieved via theECOVAP system (Praj’s proprietary).
ECOVAP is suitable for operations with effluents havinghigher solids concen-
tration and viscosity. Suspended solids slurry and precipitating salts can be han-
dled by this system with no choking issues and with fewer cleaning cycles.
A block diagram of ZLD is given in Figure 13.14.