Page 543 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 543
Zero Liquid Discharge Solutions 513
Mother liquor
(from pusher
centrifuge)
Vapor liquid
Vapor liquid
separator-II
Steam separator-I
Forced Forced Surface Vent
circulation circulation condenser condenser
evaporator evaporator
effect-I effect-II
Vacuum
pump
Feed Feed
preheater preheater
Concentrated
product
Crystallize
Feed
Steam Process
Pusher
condensate condensate centrifuge
tank tank
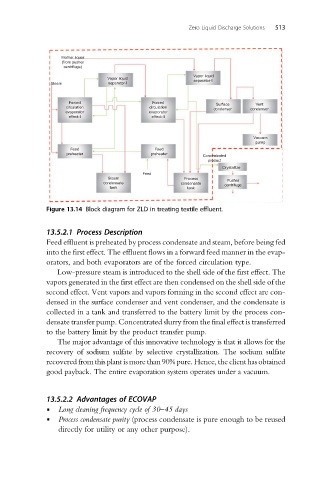
Figure 13.14 Block diagram for ZLD in treating textile effluent.
13.5.2.1 Process Description
Feed effluent is preheated by process condensate and steam, before being fed
into the first effect. The effluent flows in a forward feed manner in the evap-
orators, and both evaporators are of the forced circulation type.
Low-pressure steam is introduced to the shell side of the first effect. The
vapors generated in the first effect are then condensed on the shell side of the
second effect. Vent vapors and vapors forming in the second effect are con-
densed in the surface condenser and vent condenser, and the condensate is
collected in a tank and transferred to the battery limit by the process con-
densate transfer pump. Concentrated slurry from the final effect is transferred
to the battery limit by the product transfer pump.
The major advantage of this innovative technology is that it allows for the
recovery of sodium sulfate by selective crystallization. The sodium sulfate
recovered from this plant is more than 90% pure. Hence, the client has obtained
good payback. The entire evaporation system operates under a vacuum.
13.5.2.2 Advantages of ECOVAP
▪ Long cleaning frequency cycle of 30–45 days
▪ Process condensate purity (process condensate is pure enough to be reused
directly for utility or any other purpose).