Page 58 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 58
Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse: An Overview 41
5. Oxidation ditch
– Similar to extended aeration, except the aeration is done by brush-
type aerators, thus reducing electricity usage.
6. High rate
– Short detention time and high F/M ratio in aerator to maintain culture
in the log-growth phase.
7. Extended aeration
– Long detention time and low F/M ratio in aerator to maintain culture
in the endogenous phase.
8. Sequencing batch reactor
– Only one reactor for both aeration and sludge settlement—lower
capital cost. A special form of ASP that operates in batch mode with
sequencing.
The activated sludge process generates sludge that requires further treatment
and processing before it can be finally disposed of. A common method of dis-
posalrequiresthickeningofthewastesludge,furtherprocessingbyanaerobicor
aerobic digestion, and dewatering before land application or land disposal.
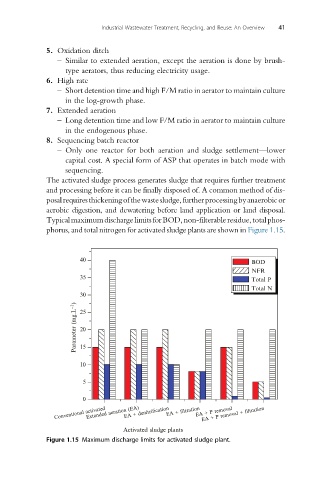
TypicalmaximumdischargelimitsforBOD,non-filterableresidue,totalphos-
phorus, and total nitrogen for activated sludge plants are shown in Figure 1.15.
40
BOD
NFR
35 Total P
Total N
30
Parameter (mg.L –1 ) 25
20
15
10
5
0
Extended aeration (EA)
Conventional activated EA + denitrification EA + filtration EA + P removal
EA + P removal + filtration
Activated sludge plants
Figure 1.15 Maximum discharge limits for activated sludge plant.