Page 62 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 62
Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse: An Overview 45
Biogas/
Anaerobic energy
wastewater
treatment
Aerobic
Untreated Primary wastewater Treated
wastewater treatment treatment wastewater
Solids
Solids
Anaerobic
wastewater
treatment
Biogas/
energy
Sludge for
disposal
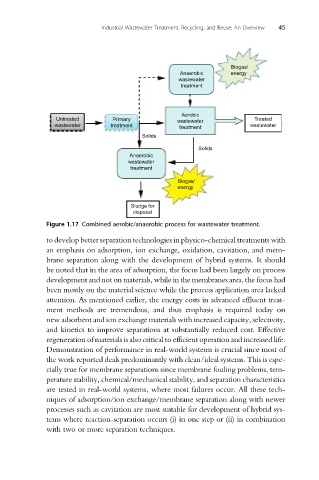
Figure 1.17 Combined aerobic/anaerobic process for wastewater treatment.
to develop better separation technologies in physico-chemical treatments with
an emphasis on adsorption, ion exchange, oxidation, cavitation, and mem-
brane separation along with the development of hybrid systems. It should
be noted that in the area of adsorption, the focus had been largely on process
development and not on materials, while in the membranes area, the focus had
been mostly on the material science while the process application area lacked
attention. As mentioned earlier, the energy costs in advanced effluent treat-
ment methods are tremendous, and thus emphasis is required today on
new adsorbent and ion exchange materials with increased capacity, selectivity,
and kinetics to improve separations at substantially reduced cost. Effective
regeneration of materials is also critical to efficient operation and increased life.
Demonstration of performance in real-world systems is crucial since most of
the work reported deals predominantly with clean/ideal systems. This is espe-
cially true for membrane separations since membrane fouling problems, tem-
perature stability, chemical/mechanical stability, and separation characteristics
are tested in real-world systems, where most failures occur. All these tech-
niques of adsorption/ion exchange/membrane separation along with newer
processes such as cavitation are most suitable for development of hybrid sys-
tems where reaction-separation occurs (i) in one step or (ii) in combination
with two or more separation techniques.