Page 28 - Injection Molding Advanced Troubleshooting Guide
P. 28
1.4 Troubleshooting Methodology 9
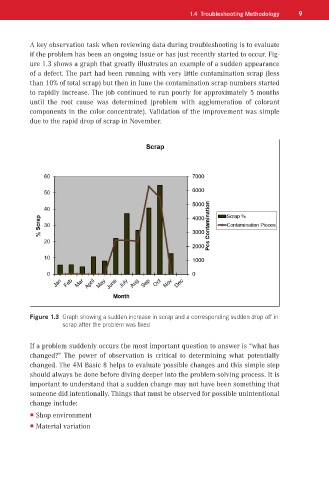
A key observation task when reviewing data during troubleshooting is to evaluate
if the problem has been an ongoing issue or has just recently started to occur. Fig-
ure 1.3 shows a graph that greatly illustrates an example of a sudden appearance
of a defect. The part had been running with very little contamination scrap (less
than 10% of total scrap) but then in June the contamination scrap numbers started
to rapidly increase. The job continued to run poorly for approximately 5 months
until the root cause was determined (problem with agglomeration of colorant
components in the color concentrate). Validation of the improvement was simple
due to the rapid drop of scrap in November.
Figure 1.3 Graph showing a sudden increase in scrap and a corresponding sudden drop off in
scrap after the problem was fixed
If a problem suddenly occurs the most important question to answer is “what has
changed?” The power of observation is critical to determining what potentially
changed. The 4M Basic 8 helps to evaluate possible changes and this simple step
should always be done before diving deeper into the problem-solving process. It is
important to understand that a sudden change may not have been something that
someone did intentionally. Things that must be observed for possible unintentional
change include:
Shop environment
Material variation