Page 312 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry - Fundamentals and Applications
P. 312
M~ltiple-Colle~tor ICP-MS 299
Sample
Con
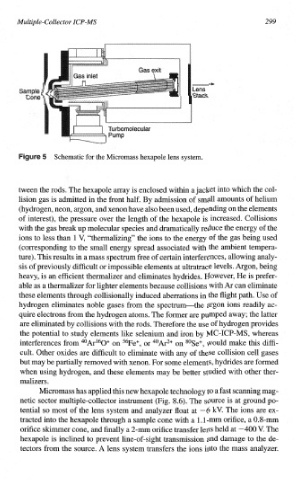
Schematic for the Micromass hexapole lens system.
tween the rods. The hexapole array is enclosed within a jacket into which the col-
lision gas is admitted in the front half. By admission of small amounts of helium
(hydrogen, neon, argon, and xenon have also been used, depending on the elements
of interest), the pressure over the length of the hexapole is increased. Collisions
with the gas break up molecular species and dramatically reduce the energy
the
of
ions to less than 1 V, “themalizing” the ions to the energy of the gas being used
(corresponding to the small energy spread associated with the ambient tempera-
ture). This results in a mass spectrum free of certain interferences, allowing analy-
sis of previously difficult or impossible elements at ultratrace levels. Argon, being
is
heavy, is an efficient thermalizer and eliminates hydrides. However, He prefer-
able as a thermalizer for lighter elements because collisions with Ar can eliminate
these elements through collisionally induced aberrations in the flight path. Use of
hydrogen eliminates noble gases from the spectrum-the argon ions readily ac-
quire electrons from the hydrogen atoms. The former are pumped away; the latter
are eliminated by collisions with the rods. Therefore the use of hydrogen provides
the potential to study elements like selenium and iron by MC-ICP-MS, whereas
interferences from 40Ay160+ on 56Fe+, or 40Ar2+ on would make this diffi-
cult. Other oxides are difficult to eliminate with any of these collision cell gases
but may be partially removed with xenon. For some elements, hydrides are formed
when using hydrogen, and these elements may be better studied with other ther-
rnalizers.
Micromass has applied this new hexapole technology to fast scanning mag-
a
netic sector multiple-collector instrument (Fig. 8.6). The source is at ground po-
tential so most of the lens system and analyzer float at -6 kV. The ions are ex-
tracted into the hexapole through a sample cone with a 1.1-m orifice, a 0.8-mm
orifice skimmer cone, and finally
a 2-mm orifice transfer lens held at -400 V. The
hexapole is inclined to prevent line-of-sight transmission and damage to the de-
tectors from the source. A lens system transfers the ions into the mass analyzer.