Page 210 - Instant notes
P. 210
Physical chemistry 196
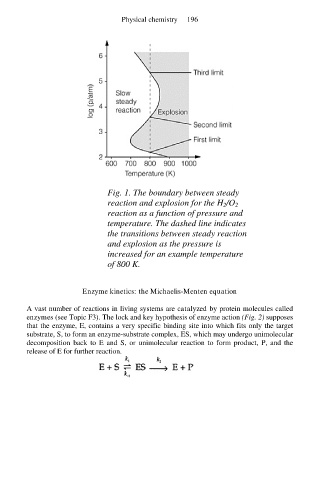
Fig. 1. The boundary between steady
reaction and explosion for the H 2/O 2
reaction as a function of pressure and
temperature. The dashed line indicates
the transitions between steady reaction
and explosion as the pressure is
increased for an example temperature
of 800 K.
Enzyme kinetics: the Michaelis-Menten equation
A vast number of reactions in living systems are catalyzed by protein molecules called
enzymes (see Topic F3). The lock and key hypothesis of enzyme action (Fig. 2) supposes
that the enzyme, E, contains a very specific binding site into which fits only the target
substrate, S, to form an enzyme-substrate complex, ES, which may undergo unimolecular
decomposition back to E and S, or unimolecular reaction to form product, P, and the
release of E for further reaction.